The Saudi Arabian currency symbol, SAR, is a crucial aspect of traveling or doing business in the country. It's used to represent the Saudi riyal, the official currency of Saudi Arabia.
The SAR is divided into 100 halalas, although the halala is no longer in circulation. This is a key fact to keep in mind when dealing with currency exchange or transactions in Saudi Arabia.
The SAR is pegged to the US dollar, with a fixed exchange rate of 3.75 SAR to 1 USD. This stability makes it easier for tourists and businesses to navigate the currency.
In Saudi Arabia, the SAR is widely accepted and used in daily transactions, including shopping, dining, and paying bills.
For your interest: Where to Exchange Mexican Money for American Money
Exchange Rates and Conversions
The Saudi Arabian currency symbol is the riyal, denoted by the abbreviation SAR. The riyal has been pegged to the IMF's special drawing rights (SDRs) since June 1986, with a fixed exchange rate of 1 U.S. dollar to 3.75 riyals.
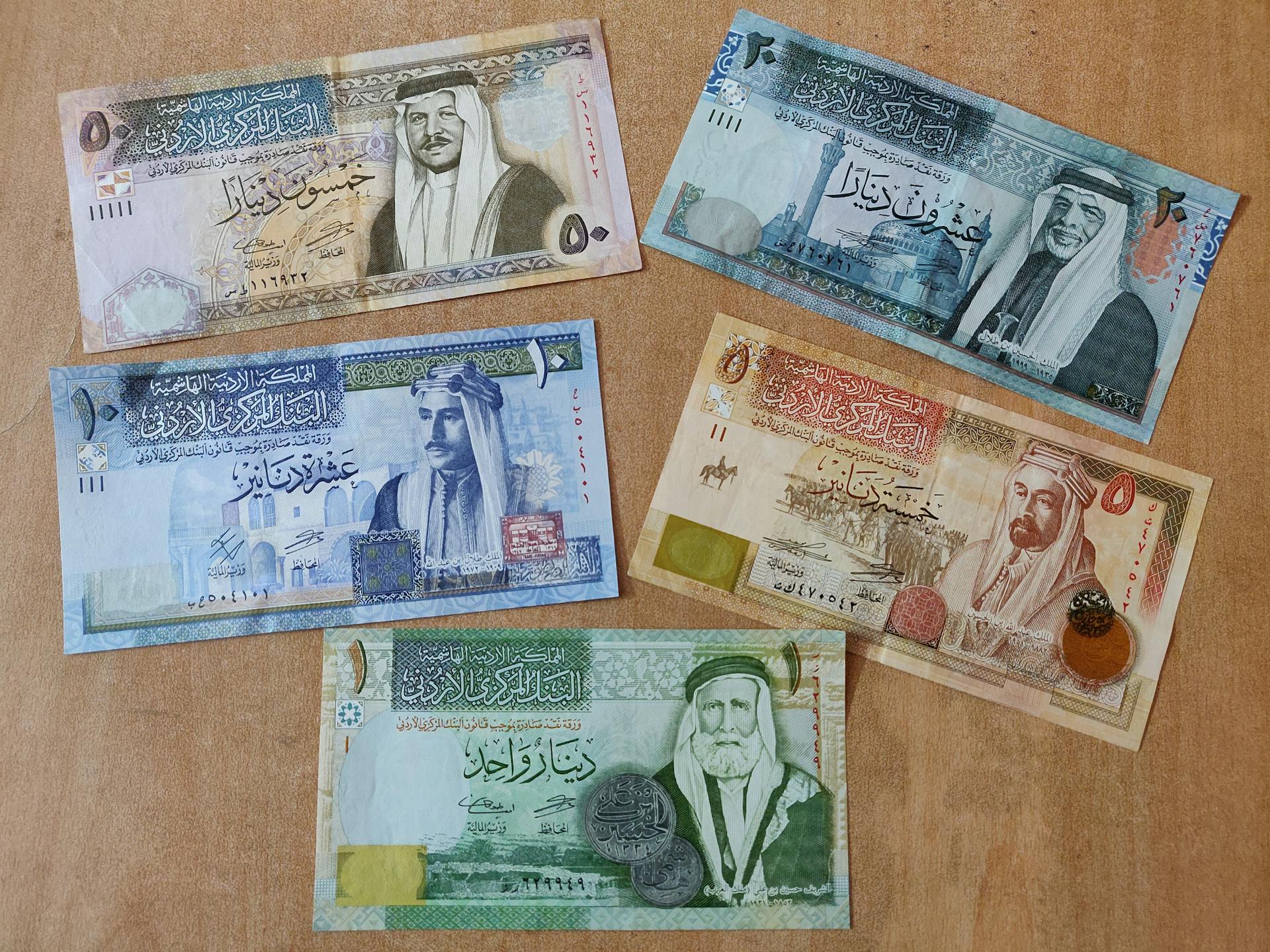

The Saudi riyal has a minor unit called the halala, which is 1/100 of a riyal. You can find coins and banknotes in various denominations, including 1, 5, 10, 25, and 50 halalas, as well as 1 and 2 riyals.
The Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) is the central bank responsible for managing the country's currency. The riyal is widely used in Saudi Arabia and can be exchanged for other currencies at banks and currency exchange offices.
Here are some common exchange rates for the Saudi riyal:
Keep in mind that exchange rates can fluctuate over time due to various economic, political, and market factors. It's essential to stay up-to-date with the current exchange rate when traveling to or doing business in Saudi Arabia.
Related reading: Exchange Currency Houston
Understanding the Currency
The Saudi Riyal (SAR) has a rich history dating back to 1932 when the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was established. It was initially based on a bimetallic monetary system using British gold sovereigns and silver Riyals.
In 1952, the monetary system was reformed to use a single currency, the Saudi Riyal, which was backed by Saudi gold guineas equivalent to the British gold sovereign until 1959. This change marked a significant shift in the country's financial landscape.
The Riyal was pegged to the Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) in June 1986, but its value is now fixed at 1 U.S. dollar = 3.75 riyals, making it a stable currency in the region.
Banknotes

The banknotes of Saudi Arabia have a fascinating history. In 1953, the Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency (SAMA) began issuing Hajj Pilgrim Receipts for 10 riyals, which were initially intended for use by pilgrims.
These receipts were later replaced by regular banknotes in 1961, which came in denominations of 1, 5, 10, 50, and 100 riyals. The Pilgrim Receipts were withdrawn in 1965.
500 riyal notes were introduced in 1983, marking a significant milestone in the country's currency history. The design of banknotes has also evolved over time, with the 6th series featuring King Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud.
The 20 riyal note, for example, measures 152×69 mm and has an olive green and gray color scheme. It features a portrait of King Salman and the logo of the G20 on the front.
The 200 riyal note, on the other hand, measures 163×73 mm and has a gray, purple, and green color scheme. It features a portrait of King Abdulaziz al-Saud and the logo of Saudi Vision 2030 on the front.
Here's a summary of the banknotes issued by SAMA:
Understanding the SAR
The Saudi riyal, or SAR, is the official currency of Saudi Arabia, and it's pegged to the US dollar at a fixed exchange rate of 3.75 SAR to 1 USD since 1986. This means that the value of the SAR is directly tied to the value of the US dollar.

The SAR is divided into 100 halalas, with coins and banknotes available in various denominations, including 1, 5, 10, 25, and 50 halalas, as well as 1, 2, 5, 10, 50, and 100 riyals. The Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) is the central bank responsible for managing the SAR.
The SAR is widely accepted in Saudi Arabia and is used for all transactions, including buying goods and services, paying bills, and transferring money. However, it's not widely traded on the foreign exchange market, which means that its value can be affected by economic and political factors in Saudi Arabia and the US.
Here are some common exchange rates for the SAR:
These exchange rates are subject to change and may vary depending on the currency exchange provider and the current market conditions.
The SAR is a fiat currency, meaning that it has no intrinsic value and is not backed by any physical commodity. Instead, its value is determined by supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. This means that the value of the SAR can fluctuate over time, affecting the purchasing power of the currency.
Overall, understanding the SAR is essential for anyone doing business or traveling to Saudi Arabia, as it's the official currency of the country.
See what others are reading: Argentina Fx Rate
Volatile Oil Market

The oil market can be a wild ride, and its connection to currency is no exception. Oil prices plummeted in 2016, causing a ripple effect in the currency market.
A devaluation of the Riyal was a real possibility, but it never came to pass. SAMA, the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority, ultimately decided not to shift the peg.
Oil prices rebounded in 2016, alleviating some of the pressure on the currency market. This was a big relief for countries that rely heavily on oil exports.
Saudi Arabia came to an agreement with the US to purchase oil from the kingdom. With the proceeds, Saudi Arabia would buy US Treasuries, further stabilizing the currency market.
In the end, Saudi Arabia agreed to price its oil in US dollars, a move that helped to stabilize the currency market.
If this caught your attention, see: Foreign Currency Exchange Investment
Currency in Modern Saudi Arabia
In modern Saudi Arabia, the official currency is the Saudi riyal, denoted by the symbol "﷼" or SAR.

The Saudi riyal is divided into 100 halalas, a smaller unit of currency that is no longer in circulation.
The currency symbol "﷼" is used to represent the Saudi riyal in financial transactions and everyday commerce.
The Saudi government has taken steps to promote the use of digital payments, with many businesses now accepting credit and debit cards.
The use of cash is still prevalent in Saudi Arabia, with many transactions taking place in cash, especially for smaller purchases.
Expand your knowledge: Currency Use in Brazil
Sources
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saudi_riyal
- https://wise.com/us/currency-converter/currencies/sar-saudi-riyal
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/forex/s/sar-saudi-riyal.asp
- https://www.monito.com/en/what-is-the-currency-in/saudi-arabia
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57073395/how-to-customize-the-currency-symbol-accordingly-with-the-language-country-code
Featured Images: pexels.com