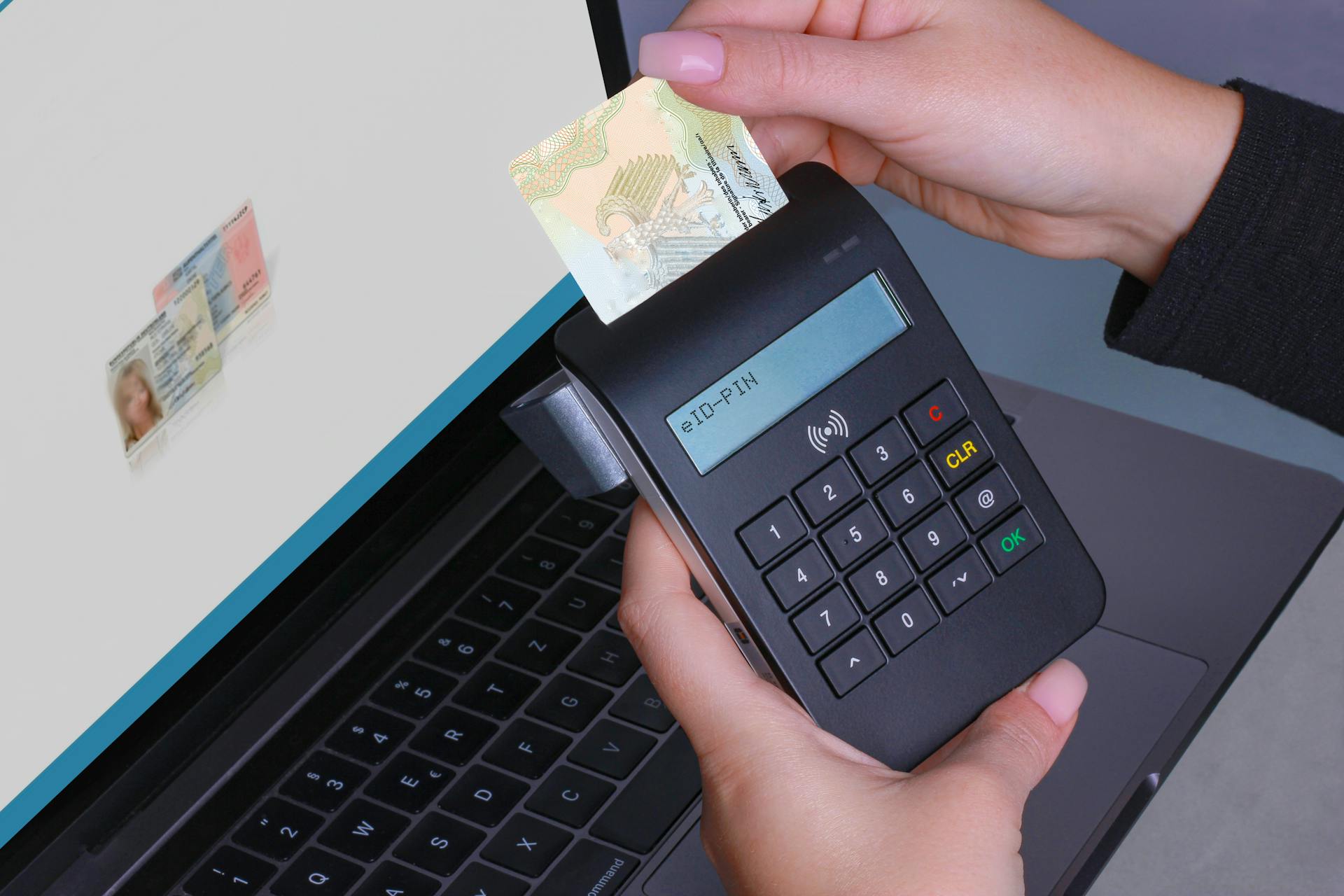
In the financial industry and banking, KYC protocols are a crucial aspect of preventing money laundering and terrorist financing. These protocols require financial institutions to verify the identity of their customers and maintain records of their transactions.
One of the key challenges in implementing KYC protocols is the need to balance customer convenience with regulatory requirements. Financial institutions must ensure that their KYC processes are efficient and do not delay transactions, while also meeting the strict guidelines set by regulatory bodies.
Financial institutions use various methods to verify customer identities, including document-based verification, biometric authentication, and data analytics. These methods help to reduce the risk of identity theft and ensure that customers are who they claim to be.
KYC protocols also involve ongoing monitoring of customer transactions to detect suspicious activity. This can include monitoring for unusual transaction patterns, large cash transactions, or transactions that involve countries or individuals on sanctions lists.
Explore further: Kyc Identification
What Is Know-Your-Customer?
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a set of identity verification procedures required by law for virtual asset service providers. KYC processes enable criminal investigators to connect pseudonymous cryptocurrency addresses to real-world entities in the event of a crime.
In traditional finance, valid credentials include ID card validation, face verification, and biometric authentication. Many banks require proof of address, such as a copy of a recent utility bill.
KYC requirements in the crypto industry vary, but most exchanges require new customers to share their full legal name, government-issued ID, and up-to-date address information during onboarding.
The following information is typically required during the KYC process:
- Legal name
- Birthdate
- Address
- National ID number
Each country has different KYC requirements, with some calling for ID documents and others requiring customers to fill out an online form to get an account.
What Is Know-Your-Customer?
Know-Your-Customer (KYC) is a set of procedures critical to assessing customer risk and is legally required to comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws.
Consider reading: Know Your Customer News
KYC involves knowing a customer's identity, financial activities, and risk. This is especially important in the cryptocurrency world, where the anonymity of transactions can make it harder to identify suspicious activity.
During the KYC process, cryptocurrency exchanges obtain identifying information such as a customer's legal name, birthdate, address, and national ID number. Each country has different KYC requirements, so the process may vary depending on where you are.
In the United States, for example, crypto companies may require customers to fill out an online form to get an account, while in other countries, customers may need to provide ID documents. Behind the scenes, the crypto company uses an identity verification service to ensure the identity is legitimate.
The goal of KYC is to protect the exchange and the financial system from money laundering, fraud, and other financial crimes. By verifying a customer's identity, crypto companies can ensure that they are not facilitating illicit activities.
Here are some common identifying information required for KYC:
- Legal name
- Birthdate
- Address
- National ID number
Crypto exchanges are often legally obligated to preserve account information with advanced security technology, making the KYC process a standard and safe practice.
What Is for?
As part of the broader Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, Know-Your-Customer (KYC) is a crucial component that helps prevent illicit funds from entering the legitimate financial system.
Crypto AML regulations require exchanges to implement KYC as part of their compliance efforts.
KYC involves verifying the identity of customers to ensure they are who they claim to be, and it's an essential step in preventing money laundering.
To be compliant with AML regulations, exchanges must create and enable policies, training, designated responsibilities, and review procedures as part of their KYC implementation.
Screening accounts against watchlists is also a key aspect of KYC, as it helps identify and flag potentially suspicious activity.
Check this out: Part 500 Nydfs
Importance and Benefits
Implementing KYC protocols is essential to the longevity of cryptocurrency, as it helps decrease customer risk factors and enhance fraud prevention.
KYC regulations protect cryptocurrency systems by decreasing customer risk factors, enhancing fraud prevention, and prioritizing AML standards.
Compliance with KYC regulations can increase customer confidence in crypto by creating a sense of trust and safety.
Take a look at this: Know Your Customer Uk
In fact, a comprehensive identity verification platform helps secure digital transactions for people and businesses.
Exchanges that focus on privacy, security, and compliance can find a competitive advantage and opportunities for growth.
Crypto exchanges are applying compliance frameworks to protect consumers, and this is crucial for their success.
Effective AML regulations make money laundering less profitable and more risky, and create new avenues for investigators to prosecute financial crime.
In 2020 alone, funds laundered through cryptocurrency exchanges topped $2.3 billion, highlighting the importance of AML regulations.
Effective AML processes within cryptocurrency businesses can stop many of these schemes before they even start.
By adopting new KYC measures, cryptocurrency businesses can build trust with users and regulators without sacrificing their bottom line.
Binance, a crypto exchange, found that "most people — 96%, 97% of users — go through KYC" during onboarding, showing that minor reductions in registrations can be a small price to pay for the benefits of KYC.
Take a look at this: Aml Kyc Compliance
Regulatory Requirements
Financial institutions have a Customer Identification Program (CIP) that requires collecting four pieces of identifying information about a client, including name, date of birth, address, and identification number.
CIP is part of an overall Know Your Customer (KYC) program that aims to protect and maintain the assets and privacy of consumers in the onboarding processes.
To comply with CIP, financial institutions must collect the applicant's name, address, date of birth, and social-security number or other government-issued ID numbers.
Businesses are required to provide additional information, including corporate/business registration documents, the company's registration number (CRN), and ultimate beneficial ownership (UBO) information.
The crypto travel rule is an Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulation that mandates VASPs to send, receive, and screen personal/business information when facilitating crypto transactions over a certain monetary threshold.
In the U.S., the threshold is $3,000, while in the EU, policymakers have agreed to implement a €0 threshold, requiring cryptocurrency businesses to capture information relating to the identity of the sender and recipient of every crypto transaction.
Intriguing read: Kyc Address Verification
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is a process that helps financial institutions better understand the nature of their customer's business and assess any potential risks, including involvement in illegal activity.
CDD is not technically part of a CIP, but it's an essential step in evaluating a customer's risk profile for suspicious account activity.
Consider reading: Kyc Cdd Edd
Reporting and Compliance
Reporting and compliance is a crucial aspect of KYC protocols. It involves filing a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) with the U.S.'s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) if any questionable or anomalous activity is uncovered during KYC procedures.
The BSA requires financial institutions to file a SAR within a specific timeframe. This is essential to aid in investigations and maintain the security of the institution.
Financial institutions must also keep up with changing regulations and maintain up-to-date customer records. This is to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and to aid in possible audits or investigations.
Compliance professionals must stay vigilant against fraudsters and criminals whose tactics continue to adapt and evolve. This includes being aware of the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in criminal activities and the threat it poses to identify verification.
Here are some key compliance requirements:
- Filing a SAR with FinCEN if any questionable or anomalous activity is uncovered during KYC procedures.
- Keeping up with changing regulations and maintaining up-to-date customer records.
- Staying vigilant against fraudsters and criminals whose tactics continue to adapt and evolve.
Risk Management
Risk Management is crucial for any financial institution or exchange to protect themselves and their customers from money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities. By following a risk-based approach, institutions can establish ownership thresholds and collect additional information to verify the legitimacy of their customers.
To determine the risk level of a customer, institutions should consider factors such as the complexity of their ownership structure, the industry they operate in, and the jurisdiction they are based in. For example, customers from sanctioned nations or those with a history of non-compliance may require enhanced due diligence.
Institutions should also consider the following questions when assessing a customer's risk level:
- How complex is the customer's ownership structure?
- Is the customer operating in a heavily regulated industry?
- Is the customer's home jurisdiction (or any of its neighboring jurisdictions) subject to sanctions, or home to terrorist organizations?
- Does the customer's home jurisdiction lack effective AML regulations or have high levels of corruption?
- To what extent is the customer's business cash-based?
- Has the customer taken any measures to mask the identity of its shareholders (e.g., via nominee shareholders or bearer shares)?
- Is the institution's relationship with the customer face-to-face?
By considering these factors and implementing a risk-based approach, institutions can mitigate risk, detect fraudulent activity, and streamline investigations, ultimately protecting themselves and their customers.
Discover more: Kyc Risk
Why Longevity
To ensure the longevity of cryptocurrency, KYC regulations are essential. They decrease customer risk factors, enhance fraud prevention, and prioritize AML standards.
Comprehensive identity verification platforms help secure digital transactions by protecting people and businesses. This creates a sense of trust and safety, which increases customer confidence in crypto.
Exchanges that focus on privacy, security, and compliance can find a competitive advantage and opportunities for growth.
Mitigate Risk, Detect, and Streamline Investigations
Risk management is crucial for businesses, especially in the cryptocurrency industry. To mitigate risk, detect suspicious activity, and streamline investigations, financial institutions and virtual asset service providers (VASPs) must implement effective Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures.
Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure ongoing compliance and detect suspicious activity, especially related to money laundering, terrorist financing, or financial fraud. AML procedures differ from KYC protocols in that they are specifically designed to detect and deter criminal and/or fraudulent behaviors in active accounts.
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) sets the standards for AML laws globally, and VASPs must employ AML compliance officers, require know-your-customer checks, and continuously monitor cryptocurrency transactions for suspicious activity.
To establish ownership, financial institutions should use a risk-based approach, considering factors such as the complexity of the customer's ownership structure, the customer's home jurisdiction, and the customer's business cash-based nature.
Here are some key risk factors to consider when assessing a customer-entity's AML risk:
- Complex ownership structure
- Heavily regulated industry
- Sanctioned home jurisdiction
- High corruption levels in home jurisdiction
- Cash-based business
- Masked shareholder identity
- Face-to-face relationship
By considering these risk factors and implementing effective AML and KYC procedures, financial institutions and VASPs can mitigate risk, detect suspicious activity, and streamline investigations.
Discover more: Kyc Risk Assessment
Industry and Banking
In the banking sector, KYC requires bankers to identify customers, beneficial owners of businesses, and the nature of customer relationships. This involves reviewing customer accounts for suspicious activity.
Banks must maintain and ensure the accuracy of customer accounts. They also have to review customer accounts for suspicious and illegal activity.
Regulators are increasing requirements for the Travel Rule, which would establish rules around originator and beneficiary information to monitor transactions. This is in response to the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations.
Different industry groups are working to create coordinated systems to comply with the Travel Rule. This will help to better protect the digital transaction space.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are mathematically provable as unique, and their ownership is verifiable on a public blockchain. This makes them a way to bring foundational business concepts into developing web 3.0 platforms.
Without KYC, money launderers could convert tainted funds into NFTs to hide their assets or cover a money trail with multiple transactions. This is a major concern for regulators.
Custodial crypto wallets have a third party that controls the private keys and holds more responsibility for fund security. Noncustodial wallets, on the other hand, give consumers total control over their private keys and funds.
KYC requirements around anonymous crypto wallets are not defined, but both the U.S. and the EU are starting to investigate. This is a sign that regulators are taking a closer look at the issue.
A different take: Crypto Exchanges That Don't Require Kyc
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three 3 components of KYC?
The three main components of KYC are: Customer Identification Program (CIP), Customer Due Diligence (CDD), and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD). These components work together to verify customers and assess their risk and financial profiles.
What is KYC protocol?
KYC protocol is a set of processes that verifies the identity of customers and ensures they're acting legally. It helps banks and financial institutions prevent financial crimes and ensure secure transactions.
What are the 4 steps of KYC?
The 4 steps of Know Your Customer (KYC) are: Customer Identification Program (CIP), Customer Due Diligence (CDD), Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD), and Ongoing Monitoring. These steps help businesses verify and assess the risk of their customers to prevent financial crimes and ensure compliance with regulations.
What is mandatory for KYC?
For KYC, you'll need to provide proof of identity (Aadhaar, passport, etc.) and proof of address (Aadhaar card, utility bills, etc.). A PAN card and recent photo are also typically required.
What are the tasks of KYC?
KYC's main tasks are to identify and assess customers with higher risk profiles, preventing them from accessing sensitive financial services. This helps prevent financial crimes and protects both banks and customers from potential harm.
Sources
- https://www.trulioo.com/industries/crypto-identity-verification/kyc
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/k/knowyourclient.asp
- https://legal.thomsonreuters.com/blog/5-essential-steps-for-kyc-aml-onboarding-and-compliance/
- https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/what-is-aml-and-kyc-for-crypto/
- https://corpgov.law.harvard.edu/2016/02/07/fincen-know-your-customer-requirements/
Featured Images: pexels.com