Firms create value for their customers and stakeholders through a range of activities.
These activities can be categorized into three main types: primary, secondary, and tertiary activities. Primary activities are directly involved in the production of a product or service, such as research and development, design, and production.
Secondary activities support the primary activities, including logistics and supply chain management, marketing and sales, and human resources.
Tertiary activities focus on the after-sales support and services, like customer service, warranty, and maintenance.
Related reading: Lifestyle Activities
Value Creation Activities
Value creation activities are the backbone of a successful business strategy. Understanding customer needs is key to value creation, and organizations must tailor their offerings effectively to meet these needs.
Inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and services are the five primary activities that generate higher profits. These activities form the foundation of a company's value chain.
Here are the primary activities in more detail:
- Inbound logistics include receiving, warehousing, and managing inventory.
- Operations involve procedures for converting raw materials into a finished product.
- Outbound logistics include activities to distribute a final product to a consumer.
- Marketing and sales include strategies to enhance visibility and target appropriate customers.
- Service includes programs to maintain products and enhance the consumer experience.
Innovation and Differentiation
Innovation and differentiation are critical elements of value creation. They help businesses stay competitive and lead their respective industries.
In today's fast-paced business environment, innovation is an ongoing process that involves identifying opportunities for improvement and implementing changes to stay competitive. Continuous innovation can include technological advancements, new product features, or even novel solutions to existing problems.
Understanding customer needs is vital in creating products or services that resonate with the target audience. Regular feedback and engagement with customers can guide the innovation process.
To create unique value, businesses must differentiate themselves from the competition. This can be achieved through superior quality, distinct features, or a one-of-a-kind customer experience.
Here are some key aspects of innovation and differentiation:
- Continuous innovation involves identifying opportunities for improvement and implementing changes to stay competitive.
- Adaptation to market dynamics is essential to stay attuned to market shifts and emerging trends.
- A customer-centric approach is vital in creating products or services that resonate with the target audience.
- Differentiation is about standing out from the competition and creating unique value propositions.
- Sustainability is an important aspect of innovation, as it can lead to long-term benefits such as cost reduction and eco-conscious customer attraction.
By prioritizing innovation and differentiation, businesses can position themselves as leaders in their industry and open up new revenue streams.
Primary Activities
Primary activities are the foundation of a company's value creation strategy. These activities are essential for adding value and creating a competitive advantage.
Inbound logistics include functions like receiving, warehousing, and managing inventory. This process ensures that raw materials and goods are properly stored and delivered to the right place at the right time.
Recommended read: A Firm's Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities Includes
Operations involve procedures for converting raw materials into a finished product. This includes manufacturing, assembly, and testing to ensure the product meets quality standards.
Outbound logistics include activities to distribute a final product to a consumer. This can be done through various channels, such as shipping, transportation, and delivery.
Marketing and sales strategies aim to enhance visibility and target appropriate customers. This includes advertising, promotion, and pricing to attract and retain customers.
Service programs focus on maintaining products and enhancing the consumer experience. This includes customer service, maintenance, repair, refund, and exchange.
Here are the five key primary activities that generate higher profits:
Support Activities
Support Activities play a crucial role in making primary activities more efficient. They are often denoted as overhead costs on a company's income statement.
These support activities can be categorized into four main areas: Procurement, Technological Development, Human Resources (HR) management, and Infrastructure. Procurement is concerned with obtaining raw materials for a company.

A company's ability to obtain raw materials efficiently can greatly impact its operations. Technological Development is used at a firm's research and development (R&D) stage, where manufacturing techniques and processes are designed and automated.
Companies with efficient R&D stages tend to have an edge over their competitors. Human Resources (HR) management involves hiring and retaining employees who will fulfill the firm's business strategy and help design, market, and sell the product.
Effective HR management can benefit multiple primary activities, such as operations, marketing, and sales. Infrastructure includes company systems and the composition of its management team – such as planning, accounting, finance, and quality control.
Here are the four support activities:
- Procurement
- Technological Development
- Human Resources (HR) management
- Infrastructure
Porter's Model
Porter's Model is a strategic management tool that helps businesses analyze their value chain. It's a framework for understanding how a company creates value and gains a competitive advantage.
Michael Porter, a renowned business strategist, developed this model in his 1985 book "Competitive Advantage." He identified five primary activities that are essential to creating value.
For another approach, see: Lemonade Insurance Business Model

These primary activities are the foundation of Porter's Model. They include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service. Each of these activities plays a crucial role in creating value for the customer.
Porter's Model also includes secondary activities that support the primary activities. These secondary activities are essential for the smooth functioning of the primary activities. For example, human resource management can play a role in operations, marketing, and sales.
By understanding and effectively implementing Porter's Model, businesses can gain a competitive edge in the market. It's a powerful tool for analyzing a company's value chain and identifying areas for improvement.
Curious to learn more? Check out: Social Media Marketing Agency
Business Strategy and Models
Business strategy is all about crafting a plan to achieve success, and businesses use various approaches to do so. In strategic management, businesses use a variety of approaches to craft a business level strategy.
Understanding the competitive landscape is key to developing a winning strategy. In business competition, understanding and effectively implementing strategic frameworks are crucial for success.
You might like: Value Creation Strategy

A business level strategy is not just about competing, but also about creating value for customers. The value creation activities of a firm are categorized as cost leadership, differentiation, and focus.
Businesses can choose from different types of business level strategies, such as cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. These strategies are designed to help businesses succeed in their respective markets.
Cost leadership involves being the lowest-cost producer in the market, which can be achieved through efficient operations and supply chain management. Porter’s Generic Strategies Tips for Business Competitive Strategy highlight the importance of cost leadership.
Differentiation involves creating unique products or services that appeal to specific customer needs. This can be achieved through innovation and marketing efforts.
Focus involves targeting a specific market segment or niche, where a business can differentiate itself and create value for customers. Business Level Strategy: Examples & Types for Business Strategy Success shows that focus is a viable strategy for businesses.
Ultimately, the choice of business level strategy depends on the company's goals, resources, and market conditions.
A different take: Types of Company Growth
Co-Creation and Creation

Value creation is a crucial aspect of any business, and it's essential to understand the key components that drive it. Understanding Customer Needs is the foundation of value creation, allowing organizations to tailor their offerings effectively.
To create value, organizations must leverage their core strengths and competencies, which are the building blocks of innovation. Innovation fuels value creation by introducing new products, services, or processes that address evolving market demands.
Value creation can be categorized into two main types: Value Creation and Value Co-Creation. Value Creation focuses on how an organization produces and delivers value, while Value Co-Creation emphasizes collaboration with customers and other stakeholders.
A key differentiator between Value Creation and Value Co-Creation is that Value Co-Creation involves actively involving customers in the value generation process, often leading to more personalized and innovative solutions.
Here's a brief comparison of Value Creation and Value Co-Creation:
By understanding the difference between Value Creation and Value Co-Creation, organizations can develop a more effective value creation strategy, one that incorporates the needs and feedback of their customers.
Consider reading: Shareholder Value Creation
What Is?
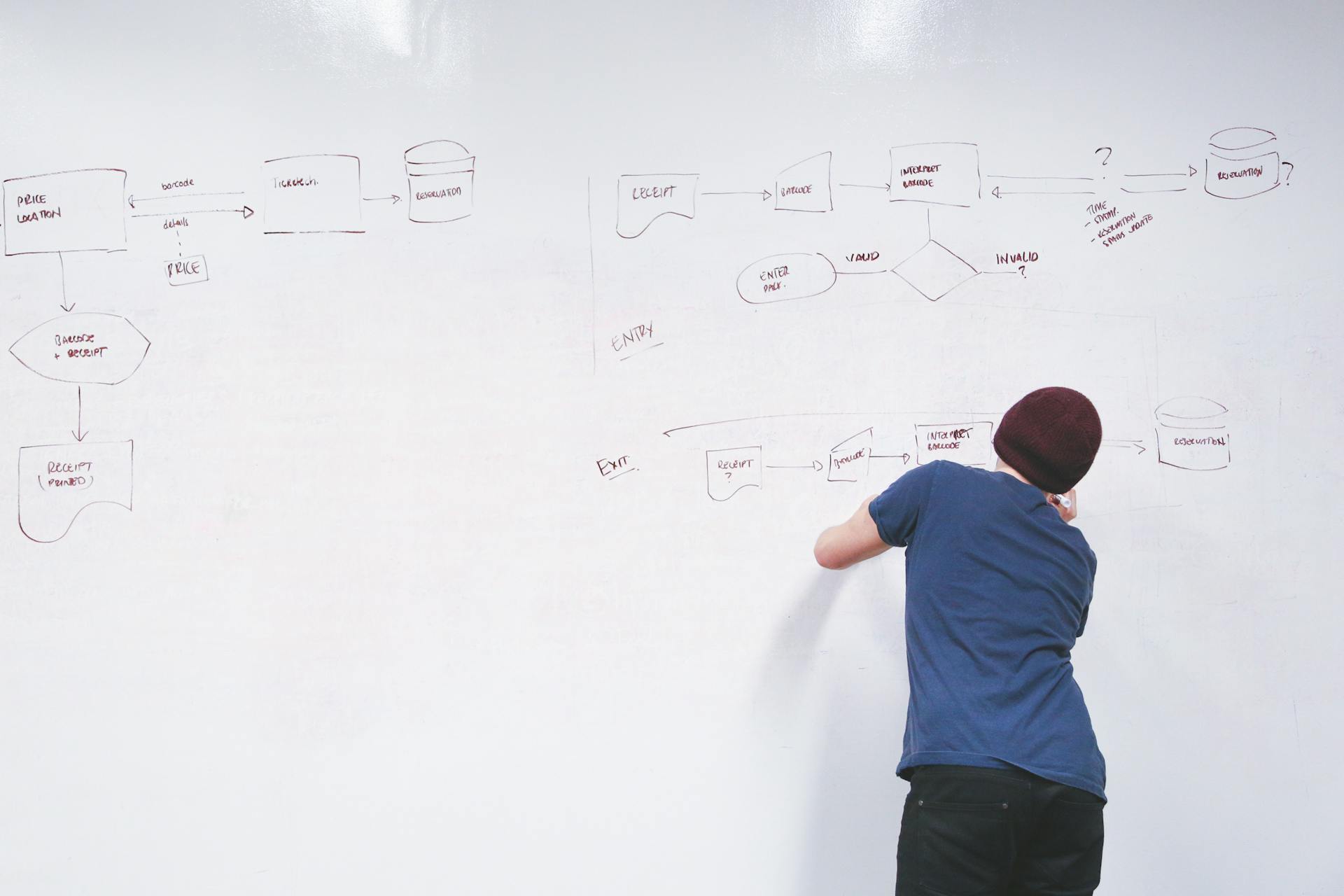

A value chain is a series of consecutive steps that go into the creation of a finished product, from its initial design to its arrival at a customer's door.
Each step in the value chain identifies where value is added, including sourcing, manufacturing, and marketing stages of production. Companies conduct a value chain analysis to increase production efficiency and deliver maximum value for the least possible cost.
Value creation is the process of generating additional value through innovation, efficient operations, or customer-centric approaches. This expands the overall value pool.
Value capture, on the other hand, involves retaining a portion of the value created as profit or return on investment, focusing on the organization's ability to capture a share of the value it contributes to.
Here's a summary of the key value creation activities of a firm:
- Value creation through innovation
- Value creation through efficient operations
- Value creation through customer-centric approaches
These activities help a firm expand the overall value pool, which is essential for its success.
Analysis and Steps
To conduct a value chain analysis, you need to follow these steps: identify primary and secondary value chain activities, determine the values and costs of those activities, and identify competitive advantage opportunities. According to Harvard Business School, this is the foundation of a value chain analysis.
To break it down further, here are the key activities involved in value chain analysis:
- Identify primary and secondary value chain activities
- Determine the values and costs of those activities
- Identify competitive advantage opportunities
Regularly assessing and measuring the impact of your value creation efforts is also crucial. This involves setting clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), collecting and analyzing data, and reporting on progress.
Measurement
Measurement is a crucial step in analysis and steps. It involves regularly assessing and measuring the impact of your value creation efforts to ensure they align with strategic objectives.
Defining clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for measuring value creation. These indicators should be directly tied to the strategic objectives of the organization.
Businesses should establish robust data collection mechanisms to gather relevant information related to their value creation efforts. This data can come from various sources, including customer surveys, financial reports, and operational data.
Take a look at this: How GPS & Telematics Data Can Help Your Fleet

Regular reporting is necessary to maintain a proactive approach to value creation. Organizations should have processes in place to compile and analyze data at regular intervals, whether it’s on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis.
Here are some key aspects of regular reporting:
- Monthly: Review progress toward short-term goals and adjust strategies as needed.
- Quarterly: Evaluate progress toward medium-term goals and make adjustments to stay on track.
- Annually: Assess overall performance and make strategic decisions for the upcoming year.
Comparing your performance and value creation efforts against industry benchmarks and competitors can provide valuable insights. This is known as benchmarking.
Soliciting feedback from customers, employees, and stakeholders is a valuable part of measurement and evaluation. Feedback can reveal areas of strength and areas in need of improvement.
Steps to Analysis
To start analyzing a business, you need to break down its operations into smaller components. According to Harvard Business School, there are three key steps to value chain analysis.
First, you need to identify the primary and secondary value chain activities. This involves understanding the core functions of your business and the supporting activities that enable them to happen.
Check this out: Supply Chain Finance
Next, you need to determine the values and costs of those activities. This will help you understand where your business is generating revenue and where it's losing money.
To identify opportunities for competitive advantage, you need to analyze the value chain activities and look for areas where you can improve or innovate.
See what others are reading: Do You Need Collateral for a Business Loan
Components and Examples
The value creation activities of a firm can be categorized into several key components, which form the foundation of a successful business strategy. Understanding Customer Needs is a crucial component, as it allows organizations to tailor their offerings effectively.
To create value, organizations must identify and leverage their Core Competencies. Innovation is also essential, as it fuels value creation by introducing new products, services, or processes that address evolving market demands.
Efficient Resource Allocation is another critical component, which involves optimizing the allocation of resources, including financial, human, and technological.
Here are the key components of value creation in a concise list:
- Understanding Customer Needs
- Leveraging Core Competencies
- Innovation
- Efficient Resource Allocation
In addition to these components, a firm's value creation activities can be categorized into primary and support activities, as described in the concept of a Value Chain.
Procurement and Services

Procurement and services are essential value creation activities for a firm. Procurement involves acquiring inputs, or resources, from suppliers and vendors. This includes finding and negotiating prices for raw materials.
In the context of e-commerce, procurement is closely tied to inbound logistics, where companies look to procure materials or goods for resale. This process can significantly impact a firm's operations and profitability.
Procurement
Procurement is the acquisition of inputs, or resources, for the firm. This process involves finding and negotiating prices with suppliers and vendors.
A company's procurement strategy can significantly impact its bottom line, making it essential to get it right. Procurement is closely related to inbound logistics, where an e-commerce company would look to procure materials or goods for resale.
Procurement involves obtaining raw materials, which is crucial for the production and delivery of goods or services. In the context of e-commerce, this means sourcing products from suppliers to sell online.
Effective procurement requires a thorough understanding of the market and the ability to negotiate fair prices with suppliers. This can help companies save costs and improve their overall competitiveness.
Curious to learn more? Check out: Bank of Credit and Commerce International
Services:
Amazon's customer-centric mission has earned it high customer satisfaction ratings for its AWS cloud service. This is a great example of a company that prioritizes its customers' needs.
A simple and easy return process is a key aspect of customer satisfaction. Amazon's streamlined process makes it convenient for customers to return items.
To effectively understand your value chain, break down primary and secondary activities into sub activities. This allows for a more granular analysis of each function.
Analyzing each sub activity on its own can help compare the financial return to the time, effort, and cost required. This helps identify areas for improvement.
Connections between sub activities can be just as important as the activities themselves. An ill-advised HR hire can create issues that permeate into many different sub activities.
Technology and inbound operations can have rippling effects throughout a company's value chain. This emphasizes the importance of considering these factors when analyzing your value chain.
Evaluating trends and patterns in sub activities can reveal potential improvement opportunities. Consider the connections between sub activities to identify areas for growth.
Broaden your view: Venture X Dallas - Braniff Centre
Sources
- https://digitalleadership.com/blog/value-creation/
- https://www.deskera.com/blog/value-creation/
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/v/valuechain.asp
- https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/050115/what-are-primary-activities-michael-porters-value-chain.asp
- https://www.academia.edu/24184731/How_Do_Value_Creation_and_Competition_Determine_Whether_a_Firm_Appropriates_Value
Featured Images: pexels.com


