Futures algo trading is a highly complex and technical field, but don't let that scare you off. With the right knowledge and tools, anyone can learn to trade futures using algorithms.
Futures contracts can be traded on various exchanges, including the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE). The CME is the largest futures exchange in the world, offering a wide range of contracts.
Algorithmic trading strategies can be based on technical indicators, such as moving averages and RSI. These indicators help identify trends and patterns in market data.
The key to successful algo trading is to backtest and refine your strategies. This involves testing your algorithms on historical data to ensure they perform well in different market conditions.
Broaden your view: Ut Bot Indicators for Trading Futures
Understanding Futures Algo Trading
Futures algo trading is a strategy that uses pre-programmed algorithms to execute trades in the futures market. This approach has gained significant attention in the financial markets due to its speed and precision.

Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading or automated trading, is a powerful strategy used in futures trading to execute trades based on pre-defined rules and algorithms. This method has grabbed significant attention in the financial markets due to its speed and precision.
The futures market is composed of various key players, including hedge funds, institutional investors, large and retail traders, and commercial hedgers. These diverse participants contribute to the robustness and efficiency of the futures and underlying stock market environments.
Algorithmic trading software plays a critical role in executing trades for crypto traders. This software is designed to automate the process of buying and selling assets based on pre-programmed instructions, removing the need for manual intervention.
There are various types of algorithmic trading strategies used in the world of crypto trading, such as trend-following strategies, mean reversion strategies, arbitrage strategies, breakout strategies, scalping strategies, news-based strategies, and statistical arbitrage strategies.
Here are some key advantages of algorithmic futures trading:
- Speed and accuracy in trade execution
- Ability to backtest and refine strategies using historical data
- Optimal entry and exit point identification based on predetermined parameters
Futures trading algorithms are designed to optimize performance, react quickly to changes in the market, and take advantage of hard to manage opportunities.
Getting Started

Getting started with futures algo trading requires selecting the right platform and resources, a key element of successful implementation.
You'll want to choose an electronic trading platform that offers algorithmic trading capabilities, such as TradingView, and a supportive broker that aligns with your trading needs and objectives.
Reliability, speed, and the range of tools and features are essential considerations when selecting a platform.
To ensure success, you must also consider implementing robust risk management strategies, including setting appropriate stop-loss orders, position sizing, and diversifying trading strategies to spread risk.
Proper capital allocation is vital, and traders should aim to allocate their capital effectively, balancing risk and reward, to avoid overextending themselves financially.
Education and training are indispensable for acquiring the necessary knowledge and skills, and numerous educational resources, including online courses, webinars, and tutorials, are available to help futures traders learn about algorithmic trading and develop their expertise.
If this caught your attention, see: Forex Futures Trading Platform
Advantages and Risks
Futures algo trading offers several advantages over traditional trading methods. One of the most significant benefits is the speed and precision with which these algorithms can execute trades.
Algorithms can process vast amounts of data in real time, making split-second decisions and executing trades almost instantaneously. This capability minimizes slippage and optimizes entry and exit points, which can enhance its overall performance substantially.
Another advantage is algorithms' ability to exploit short-term market inefficiencies. They can quickly identify and capitalize on price discrepancies and other market anomalies that may be too subtle or fleeting for human traders to detect.
However, futures algo trading also comes with its fair share of challenges and risks. One major challenge is the potential for technical glitches or system failures that can disrupt trade execution or result in significant losses.
To overcome these risks, it's essential to implement strict risk management protocols, such as stop-loss orders, position sizing, and portfolio rebalancing. These tools can help shield algorithms from potential losses and ensure more error-free, disciplined, and consistent trading results.
On a similar theme: Algo Trading Algorithms
Advantages
Algorithms in futures trading bring a lot of speed to the table, allowing them to analyze vast amounts of market data and trade in milliseconds, unthinkable for human traders.

At scale, algorithms can time-sensitive market opportunities that last only seconds, and respond quickly to market changes, which means traders can win the future markets that are fierce and quick.
Accuracy is another great advantage of algorithmic trading, eliminating chances of human error like accidentally placing incorrect orders or missing an ideal trade entry.
Algorithms guarantee that the trader can run their strategies successfully and with predictability, every time without deviations or fluctuations.
The biggest and one of the most important benefits of algorithmic trading is its ability to remove emotional biases that are formed, like fear and greed, which can often be human traders' biggest problems.
Algorithms are logical and data-based, making choice based only on data and logic, rather than by emotions, allowing a trader to remain disciplined and follow their strategy without falling into common psychological traps.
Algorithms allow for efficient backtesting of strategies, which means traders can test their algorithm on historical market data in various situations to see how it would have performed.
This allows you to see where potential weak spots may be, which you can then work to work out of the strategy before risking actual capital.
Recommended read: Algorithmic Trading Winning Strategies and Their Rationale

Algorithmic futures trading excels at identifying optimal entry and exit points based on predetermined parameters, making it a powerful tool for traders.
By automating the trading process, algorithms eliminate the impact of human error and emotions, such as fear and greed, which can lead to poor decision-making.
Algorithms can incorporate sophisticated risk management techniques by dynamically adjusting positions to control exposure and optimize returns, enhancing risk management.
Algorithms can process vast amounts of data in real time, making split-second decisions and executing trades almost instantaneously, minimizing slippage and optimizing entry and exit points.
By automating the trading process, algorithms can exploit short-term market inefficiencies, quickly identifying and capitalizing on price discrepancies and other market anomalies that may be too subtle or fleeting for human traders to detect.
Risks and Considerations
High market volatility can lead to significant losses for trading algorithms, especially those using high-frequency trading strategies that rely on capturing a small profit margin.
Suggestion: Developing High Frequency Trading Systems

System failures and connectivity issues can disrupt trading activities and result in financial losses, making robust and reliable technical infrastructure essential.
Algorithmic trading is typically subject to strict oversight to prevent market manipulation and ensure fair trading practices, requiring traders to comply with each official regulation applicable to their jurisdiction.
Traders must possess or acquire advanced technical skills and knowledge of both finance and technology to develop, monitor, and maintain sophisticated trading algorithms.
Low market liquidity can exacerbate the risks associated with trading algorithms, making it difficult to execute large orders without impacting futures prices adversely.
Stop-loss orders are a principal risk management mechanism that can automatically cause a trade to exit a position once a price reaches a given level, limiting potential losses.
Position sizing is another important part of risk management, where the algorithm decides how big each trade has to be depending on the size of the entire account and the trader’s risk tolerance.
Portfolio rebalancing is also a crucial risk management tool, where the algorithm periodically adjusts the portfolio to keep exposure to each contract or different asset class near the desired allocation subject to market conditions.

Technical glitches or system failures can disrupt trade execution or result in significant losses, making it essential to have robust and reliable technical infrastructure.
The constant need for adaptation and optimization is a significant challenge in automated trading, as financial markets are dynamic and ever-changing.
Managing risk is paramount in automated trading, requiring careful consideration of factors such as position sizing, leverage usage, stop-loss orders, and diversification within portfolios.
A fresh viewpoint: Algo Trading Automated Software
Algorithm Mechanics
Algorithmic futures trading employs a systematic process that gathers market data, analyzes it, and makes trades based on pre-defined rules. The process starts with market data gathering and analysis, which can include inputs like price levels, volume, volatility, and technical indicators.
Algorithms can monitor the market and understand when something changes and when the right time to act is. They can also join basic information like news sentiment or financial reports for additional capability in the decision-making process.
A few algorithms go by preset rules of decision making, which are planned according to the trader's strategy. These rules can include buying when the price falls at a certain level, selling when the moving average crosses, or trading according to volatility changes.

Here are some common types of algorithmic trading strategies:
- Trend-following strategies
- Mean reversion strategies
- Arbitrage strategies
- Breakout strategies
- Scalping strategies
- News-based strategies
- Statistical arbitrage strategies
To execute trades, algorithms use different types of orders, such as market orders, limit orders, or stop-loss orders. A market order is an example of buying or selling in the market immediately at the best market available price.
Algorithm Basics
Algorithmic trading algorithms are designed to analyze vast amounts of market data, including technical indicators and fundamental factors.
These algorithms generally consist of several critical components that perform key functions like data analysis, decision-making, and trade execution. They collect and process market data from various sources, such as price feeds, news, and economic reports.
In the decision-making phase, mathematical models and trading rules are applied to the analyzed data to generate trading signals, which indicate whether to buy or sell a futures contract.
Algorithms can work on tons of different inputs like price levels, volume, volatility, and technical indicators, and can be made to work on any single metric of choice.
You might like: Futures Trading Indicators Thinkorswim

A few algorithms join basic information like news sentiment or financial reports for additional capability in the decision-making process.
Algorithms use preset rules of decision making to determine whether to conduct a deal or not, which are planned according to the trader's strategy.
These rules can include buying when the price falls at some level, selling when the moving average crosses, and trading according to the volatility changes.
Algorithms implement a transparent protocol to ensure that trades are conducted fast and have little slippage, using different types of orders like market orders, limit orders, or stop-loss orders.
A market order, for example, buys or sells in the market immediately at the best market available price, while a limit order forces a trade only to be executed at some specific price or better.
Mean Reversion
Mean reversion strategies are based on the principle that asset prices tend to revert to their historical averages over time. This approach assumes that deviations from the average price are temporary and will eventually return to their mean.

Algorithms analyze historical price data to determine the average price of an asset over a specific period. They identify deviations from this average and predict when prices are likely to revert.
A mean reversion strategy involves buying assets when their prices fall significantly below the historical average and selling when prices rise significantly above the average. This is done using statistical models and indicators like Bollinger Bands and moving averages.
Here's a breakdown of the key components of a mean reversion strategy:
Mean reversion strategies benefit from a trading algorithm's ability to continuously monitor and analyze price movements quickly. This allows the algorithm to execute trades swiftly and capitalize on temporary price discrepancies.
Trend Following
Trend Following is a key strategy used in algorithmic trading, particularly in futures trading. It involves identifying and capitalizing on ongoing price trends.
Trend-following algorithms use technical analysis tools and indicators, such as moving averages, trendlines, and the Relative Strength Index (RSI), to identify the direction and strength of trends. This helps traders to make informed decisions and execute trades in the direction of the trend.
Trend-following strategies can be adapted to different time frames, allowing them to capitalize on various market conditions. This flexibility is essential in trending markets where prices exhibit clear directional movements.
Effective risk management is crucial in trend-following, as trends can reverse unexpectedly. Trend-following algorithms generally use stop-loss orders and trailing stops to protect profits and limit losses.
Trend-following strategies often involve diversifying across multiple assets and markets to spread risk and increase the probability of capturing profitable trends. This diversification helps to reduce the impact of any one trade going against the algorithm.
Here are the key components of trend-following strategies:
- Trend Identification: Algorithms use technical analysis tools and indicators to identify the direction and strength of trends.
- Momentum Trading: Once a trend is identified, the algorithm executes trades in the direction of the trend.
- Adaptive Strategies: Trend-following algorithms can adapt to different time frames, identifying short-term, medium-term and long-term trends.
- Risk Management: Trend-following algorithms use stop-loss orders and trailing stops to protect profits and limit losses.
- Diversification: Trend-following strategies often involve diversifying across multiple assets and markets.
The Mechanics Behind
Algorithmic trading algorithms are made in a systematic way that employs inputs into data, protocols of decision making and trades exactly.
These algorithms work on tons of different inputs like price levels, volume, volatility and technical indicators. You can also make them work on any single metric of choice.
Worth a look: Does Algo Trading Work

A few algorithms join basic information like news sentiment, or financial reports for additional capability in the choice making procedure.
The algorithm goes based on preset rules of decision making whether you conduct a deal or not. These rules are planned according to the trader’s strategy, such as buy when the price falls at some level, sell when the moving average crosses, as well as trade according to the volatility changes.
Being objective with the decision making process takes the emotional biases that come with human thinking out of the equation.
For its execution, an algorithm implements a transparent protocol to make sure that trades are conducted fast and have little slippage. The algorithm may use different types of orders on the basis of the strategy like market order, limit order or stop-loss order.
Here are some common types of orders used in algorithmic trading:
- Market order: Buying or selling in the market immediately at the best market available price.
- Limit order: Forcing a trade only to be executed at some specific price or better.
- Stop-loss order: Booking out of a position (automatically) if the market takes the trader in the opposite direction by a specified amount.
Risk is often managed with stop-loss orders, which book out of a position (automatically) if the market takes the trader in the opposite direction by a specified amount.
Through this seamless process, futures trading algorithms get to run code quickly while analyzing the data, making decisions, and executing trades, but trades are executed exactly the way you set the strategy up.
See what others are reading: Arkk Trades
Customizing and Developing

Customizing and developing futures trading algorithms can be a game-changer for traders, allowing them to automate and precision execute their trades. Traders can make their own algorithms or modify existing ones to fit their trading goals.
To develop or modify trading algorithms, you'll need to understand programming languages like Python, which is the most popular choice due to its simplicity and flexibility. Python has a vast ecosystem of libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and TA-Lib that make data analysis and technical indicators a breeze.
Customizing your futures trading algorithms requires programming understanding, developing strategies, and testing. Traders can use tools and platforms like MetaTrader and NinjaTrader to create algorithms based on their own way of trading the market.
Backtesting is crucial in the development process, allowing traders to run their strategies through historical data to assess performance in different market conditions. This helps traders optimize their algorithms and identify weaknesses.
Some trading platforms, like MetaTrader and NinjaTrader, offer comprehensive platforms for backtesting, developing, and deploying algorithms. These platforms provide real-time feedback and collaborative learning opportunities in live trading rooms.

You can also use platforms like Build Alpha, which provides a custom signal builder that requires no coding. This allows you to combine indicators, comparisons, operators, math functions, and parameter values to create custom signals without needing to write code.
To give you an idea of the flexibility of custom signal builders, Build Alpha's example divides the 2-period RSI by the 4-period RSI and only trades when this value is greater than 1.5. This is just one example of the many possibilities with custom signal builders.
For another approach, see: Quantitative Trading: How to Build Your Own Algorithmic Trading Business
Risk Management and Testing
Risk management is a crucial aspect of futures algo trading, and it's essential to have a systematic approach to manage risk without emotional decision-making. Stop-loss orders are a key risk management mechanism, automatically exiting a trade when a pre-defined price level is reached, limiting potential losses.
Position sizing is another important aspect of risk management, where the algorithm decides the size of each trade based on the account size and risk tolerance. This helps to prevent any one trade from wiping out the account, even in volatile market conditions.

To ensure the robustness of trading strategies, stress tests are critical. These tests include various scenarios such as vs Random, vs Shifted, vs Others, vs Noise Adjusted, Monte Carlo Simulations, Variance Testing, Delay and Liquidity Testing, and more.
Here are some key risk management tools to consider:
- Stop-loss orders
- Position sizing
- Portfolio rebalancing
- Stress testing
Risk Management
Risk Management is a crucial aspect of algorithmic futures trading. It's essential to have a solid risk management plan in place to protect your trading account from significant losses.
Stop-loss orders are a key risk management mechanism, automatically exiting a trade when a predetermined price level is reached. This helps limit potential losses and prevents emotional decision-making.
Position sizing is another critical aspect of risk management. By limiting the size of each trade, you can protect your account from large losses, even in volatile market conditions.
Portfolio rebalancing is also an important risk management tool. It involves periodically adjusting the portfolio to maintain the desired allocation to each contract or asset class, reducing concentration risk.

Technical glitches and system failures can also disrupt trade execution and result in significant losses. Constantly monitoring and adjusting your trading strategies is essential to overcome these challenges.
Some key risk management strategies include:
- Stop-loss orders
- Position sizing
- Portfolio rebalancing
- Diversification
- Continuous learning and adaptation
By implementing these risk management strategies, you can protect your trading account and achieve long-term success in algorithmic futures trading.
Overcoming Challenges and Mitigating Risks
To overcome challenges and mitigate risks in algorithmic trading, it's essential to have a robust and reliable technical infrastructure in place. This includes ensuring system failures, connectivity issues, and latency don't disrupt trading activities and result in financial losses.
Technical risks can be mitigated by implementing robust and reliable technical infrastructure. According to Example 4, this includes ensuring system failures, connectivity issues, and latency don't disrupt trading activities and result in financial losses.
Regulatory risks are also a significant consideration in algorithmic trading. Traders must comply with each official regulation applicable to their jurisdiction, refrain from illegal insider trading activities, and stay abreast of any changes in the relevant legal environment.
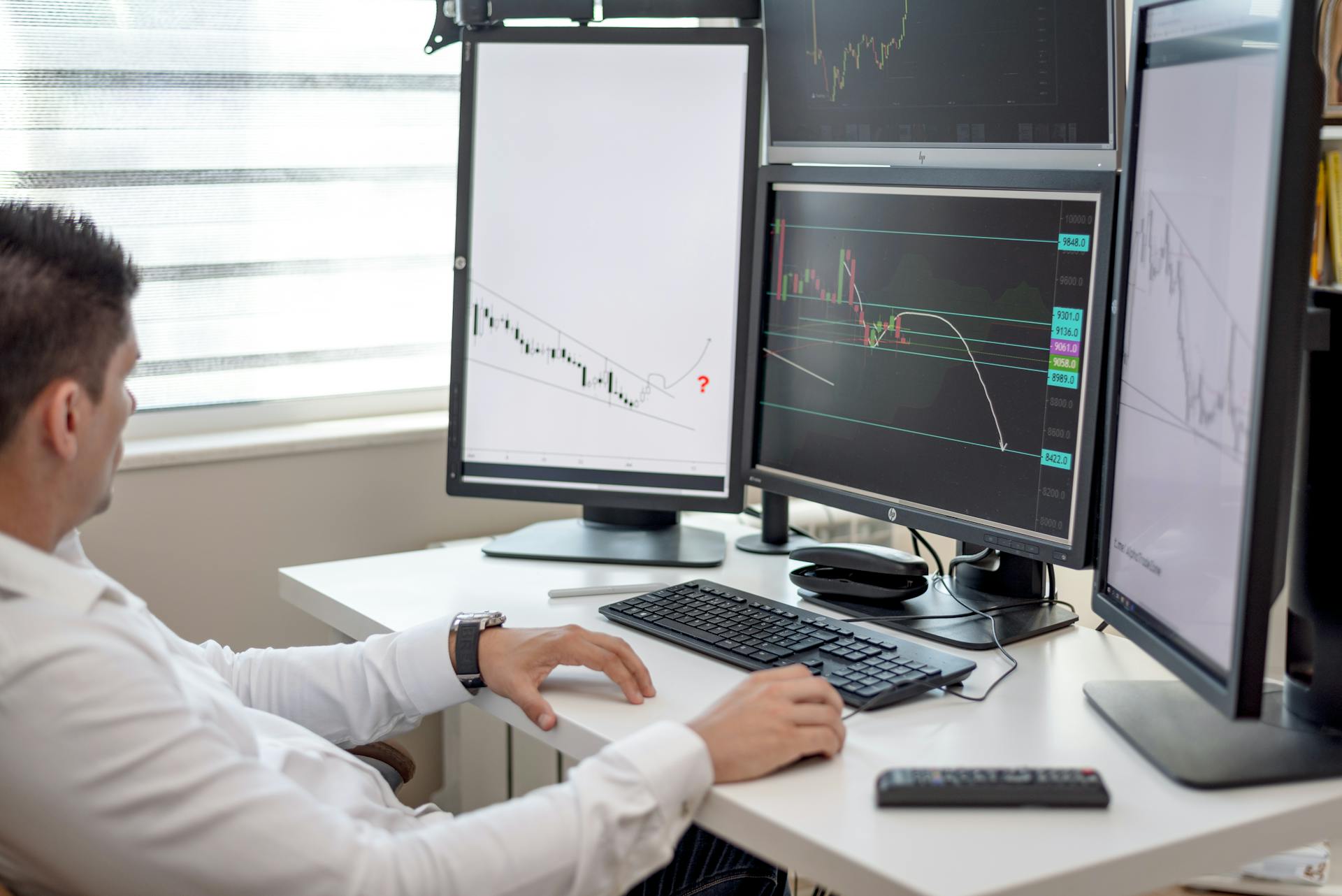

Regulatory risks can be mitigated by staying informed about regulatory changes and ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations. This is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure trading activities remain legal.
To overcome challenges and mitigate risks, traders must be vigilant about monitoring algorithm performance and make sure strategies are updated accordingly. This includes being aware of potential pitfalls in algorithmic trading, such as over-optimization, market volatility, and technical issues.
Some common challenges in algorithmic trading include algorithms being optimized too much for historical data but failing to adjust to live market conditions. This can result in poor performance when used in real-time trading.
To mitigate these risks, traders can use risk management tools such as stop-losses, which can be programmed into certain algorithms. However, these tools may not react quickly enough in a sharp market move or flash crash, amplifying risk.
The following table summarizes some common challenges and limitations in algorithmic trading:
By being aware of these challenges and limitations, traders can take steps to mitigate risks and ensure successful algorithmic trading.
Hypothetical Performance Disclaimer

Hypothetical performance results have many inherent limitations, some of which are described below. No representation is being made that any account will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those shown.
Hypothetical trading does not involve financial risk, and no hypothetical trading record can completely account for the impact of financial risk of actual trading. This is a crucial distinction to make when testing trading strategies.
One of the limitations of hypothetical performance results is that they are generally prepared with the benefit of hindsight. This means that the results are based on what happened after the fact, rather than what was actually known at the time.
The ability to withstand losses or to adhere to a particular trading program in spite of trading losses are material points which can also adversely affect actual trading results. This is a key consideration when building a trading strategy.
There are numerous other factors related to the markets in general or to the implementation of any specific trading program which cannot be fully accounted for in the preparation of hypothetical performance results. These factors can also adversely affect trading results.
Testing Spreads

Testing Spreads is a crucial part of risk management. You can test Futures spreads without any limitations, as long as the data follows the formatting guidelines accepted by Build Alpha.
You can include any columns you want, such as Date, Time, Open, High, Low, Close, Volume, and Open Int. Any columns without data can be filled with dummy values or zeroes.
Software and Tools
Futures algo trading relies on sophisticated software and tools to execute trades at high speeds and with precision. Build Alpha generates fully automate-able code for trading algorithms on various platforms, including TradeStation, NinjaTrader8, and MetaTrader4 and MetaTrader5.
Algorithmic trading software plays a critical role in executing trades, constantly monitoring market conditions and analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time to identify optimal entry and exit points for trades.
Some key software and tools used in futures algo trading include the Trendline indicator, Renko bars, and the Squeeze indicator. These tools help traders determine the prevailing trend and assess momentum, enabling them to stay in the trend for a longer period.
Here are some examples of software and tools used in futures algo trading:
- Trendline indicator
- Renko bars
- Squeeze indicator
- Trailing Stop
- SR Zones
- Trend Line
- Renko Bars
- Chart Trend Background
- Volume Delta
- Automatic Fibonacci Levels
- Volume Profile
- Futures Trading System
- Auto Trend Line
- Market Cycle
- Trend Meter
- Cloud Indicator
- AI Range Boxes
Best Software Integrations

Build Alpha is a powerful tool for traders, offering seamless integrations with various platforms to streamline their workflow. It generates fully automate-able code for all trading algorithms for a variety of Futures brokers and platforms at a click of the button.
Some of the supported platforms include TradeStation, NinjaTrader8, MultiCharts, MetaTrader4 and MetaTrader5, and Pro Real Time. These integrations enable traders to connect their algorithms to live data from TradeStation, Interactive Brokers, QuoteMedia, and Binance.
To generate code for any strategy created by Build Alpha, simply highlight the strategy and click the code generator of your choice in the lower right of the results window. This feature saves traders a significant amount of time and effort.
Here are some of the supported platforms:
- TradeStation
- NinjaTrader8
- MultiCharts
- MetaTrader4 and MetaTrader5
- Pro Real Time
By leveraging these integrations, traders can focus on developing and refining their trading strategies, rather than worrying about the technical aspects of implementation.
Software
Algorithmic trading software plays a crucial role in executing trades, refining strategies, and identifying optimal entry and exit points using algorithms.

Algorithmic trading software automates the process of buying and selling assets based on pre-programmed instructions, removing the need for manual intervention.
This software constantly monitors market conditions, analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time to identify optimal entry and exit points for trades.
Algorithmic trading software empowers crypto traders by automating trade execution and enabling them to react swiftly to market opportunities without being limited by human capabilities alone.
The Trendline indicator and Renko bars are utilized to determine the prevailing trend in algorithmic trading software.
The Squeeze indicator is employed to assess momentum, and when the bars are green and plotted above the trend line, it indicates an upward trend.
Trading with Renko bars provides traders with a precise and unambiguous method for identifying trends and reversal areas.
The system is further equipped with a color moving average and audio alerts, serving as a notification mechanism for trend changes.
Algorithmic trading software can be used to trade various futures markets, including the ES, CL, NQ, YM, GC, or Micros.
Algorithmic trading, also known as algo trading or automated trading, is a powerful strategy used in futures trading to execute trades based on pre-defined rules and algorithms.
Here's an interesting read: Placing Trades with Trading View from Tradestation
NinjaTrader 8

NinjaTrader 8 is a powerful platform that offers a range of features and tools to help traders succeed.
The NinjaTrader 8 platform is only available for futures trading and is not a free trial offering, so you'll need to purchase the software to use it.
One to two weeks is recommended to learn how to trade the signals, and it's suggested to invest at least two weeks in sim trading to get familiar with the system.
The NinjaTrader 8 platform offers a range of trading tools, including Volume Delta, Automatic Fibonacci Levels, Trailing Stop, SR Zones, Trend Line, Renko Bars, and Chart Trend Background.
Here are some of the key features of the NinjaTrader 8 platform:
It's essential to remember that futures, stocks, options, and forex trading involve large potential risks, so it's crucial to be aware of the risks and be willing to accept them before investing.
Real-World Implementation
Real-world implementation of futures algo trading requires choosing a reliable algorithmic trading software that can execute trades efficiently and accurately.

Testing and refining your trading strategies are paramount to achieve success in algorithmic futures trading, which involves backtesting historical data to evaluate how well your algorithms would have performed in different market conditions.
Identifying optimal entry and exit points based on past trends and patterns is crucial, and managing risks associated with automated trading is essential for long-term profitability.
Market Making
Market making is a strategy that provides liquidity to the market by placing both buy and sell orders around the current futures market price. This helps maintain market liquidity, allowing for smoother and more efficient trading.
Market makers continuously post buy and sell orders in the futures markets, ensuring there is always a counterparty for trades. They earn profits from the bid-ask spread, which is the difference between the buying price (bid) and the selling price (ask).
The profit for market makers comes from capturing the bid-ask spread. For example, if a market maker buys a futures contract at a bid price of $100 and sells it at an asking price of $101, they earn a profit of $1.
Market makers rely on high trading volumes and rapid turnover to execute trades and maximize their profit. The more trades executed, the greater the cumulative profit from the tight dealing spreads in the futures markets.
To mitigate their risk, market makers often lay off substantial accumulated positions with other counterparties. This helps them avoid significant exposure to market price fluctuations.
Here's a breakdown of the key components of market making:
- Liquidity Provision: Market makers continuously post buy and sell orders to ensure a counterparty for trades.
- Bid-Ask Spread: Market makers earn profits from capturing the difference between the buying and selling price.
- Volume and Turnover: High trading volumes and rapid turnover are necessary to execute trades and maximize profit.
- Risk Management: Market makers lay off accumulated positions with other counterparties to avoid exposure to market price fluctuations.
Real-World Implementation and Operations
To implement algorithmic trading strategies effectively, you need a reliable algorithmic trading software that can execute trades efficiently and accurately. This software is crucial for executing trades at lightning speed.
Testing and refining your trading strategies are paramount to achieve success in algorithmic futures trading. Backtesting historical data is essential to evaluate how well your algorithms would have performed in different market conditions.
Identifying optimal entry and exit points based on past trends and patterns is key to successful trading. By analyzing past data, you can make more informed decisions about when to buy and sell.
Managing risks associated with automated trading is essential for long-term profitability. Algorithms can be highly efficient, but they're not foolproof against unexpected market volatility or glitches.
Understanding the real-world implementation aspects of algorithmic futures trading will help you navigate this rapidly evolving landscape with confidence.
You might like: Currency Carry Trade
Case Studies and Success Stories
Futures algo trading has proven to be a lucrative field, with several notable case studies and success stories.
Renaissance Technologies, a hedge fund, has consistently outperformed the market through its Medallion Fund, achieving annualized returns of over 66% from 1988 to 2019.
Jump Trading, a proprietary trading firm, has capitalized on microsecond price movements in futures markets using advanced algorithms and cutting-edge technology.
Two Sigma Investments has achieved impressive returns across various asset classes, including futures contracts, by harnessing vast amounts of data and using machine learning techniques.
BitMEX has attracted traders who utilize algorithms to exploit short-term price swings in digital assets through unique products like perpetual swaps.
DRW Holdings' subsidiary Cumberland Mining has become one of the largest liquidity providers in the cryptocurrency space, leveraging market-making and quantitative analysis expertise.
These success stories highlight the potential of algorithmic futures trading for traders seeking consistent profits, leveraging advanced technology and data-driven strategies.
Software and Platforms

When working with futures algo trading, having the right software and platforms is crucial. Build Alpha's algorithmic trading platform offers robust features for futures trading, including access to futures data across all timeframes and the ability to choose time windows and seasonality.
Build Alpha's algorithmic trading platform offers robust features for futures trading, including economic events and data, add additional data, robustness testing, rebalance strategies, hedging, and ensemble strategies. This comprehensive approach helps traders refine their strategies and identify optimal entry and exit points.
One of the standout features of Build Alpha is its ability to generate fully automate-able code for all trading algorithms for various futures brokers and platforms. This is made possible through integrations with platforms like TradeStation, NinjaTrader8, MultiCharts, MetaTrader4 and MetaTrader5, and Pro Real Time.
To generate code for any strategy created by Build Alpha, simply highlight the strategy and click the code generator of your choice in the lower right of the results window. This makes it easy to automate trades and take advantage of market opportunities.
The following platforms are supported by Build Alpha:
- TradeStation
- NinjaTrader8
- MultiCharts
- MetaTrader4 and MetaTrader5
- Pro Real Time
Additionally, Build Alpha can connect to live data from TradeStation, Interactive Brokers, QuoteMedia, and Binance. This allows traders to view real-time position updates, live P&L, and receive alerts to saved algorithmic trading strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I trade futures with $100?
Yes, you can start trading futures with as little as $100 USD, but this is just the initial funding and not your total expense. Funding your account is just the first step in creating a comprehensive budget for your futures trading business.
Do futures trading bots work?
Yes, futures trading bots can work effectively, automating trades 24/7 based on predefined strategies and technical indicators to capitalize on market fluctuations. By leveraging these bots, traders can potentially increase their trading efficiency and profitability.
Is algo trading profitable?
Algo trading can be profitable, but its success depends on various factors, including strategy, market conditions, and expertise. Learn more about the potential benefits and challenges of algo trading
What is the best strategy for futures trading?
The best strategy for futures trading is to make a directional bet on the underlying good by going long or short futures, depending on your market analysis. Consider diversifying your approach with intra-market calendar spreads or commodity pairs trades for a more comprehensive strategy.
Sources
- https://www.benzinga.com/money/futures-trading-algorithms
- https://highstrike.com/futures-trading-algorithms/
- https://www.buildalpha.com/algorithmic-futures-trading-software/
- https://theenterpriseworld.com/understanding-algorithmic-futures-trading/
- https://www.trading123.net/product/futures-trading-system/
Featured Images: pexels.com

