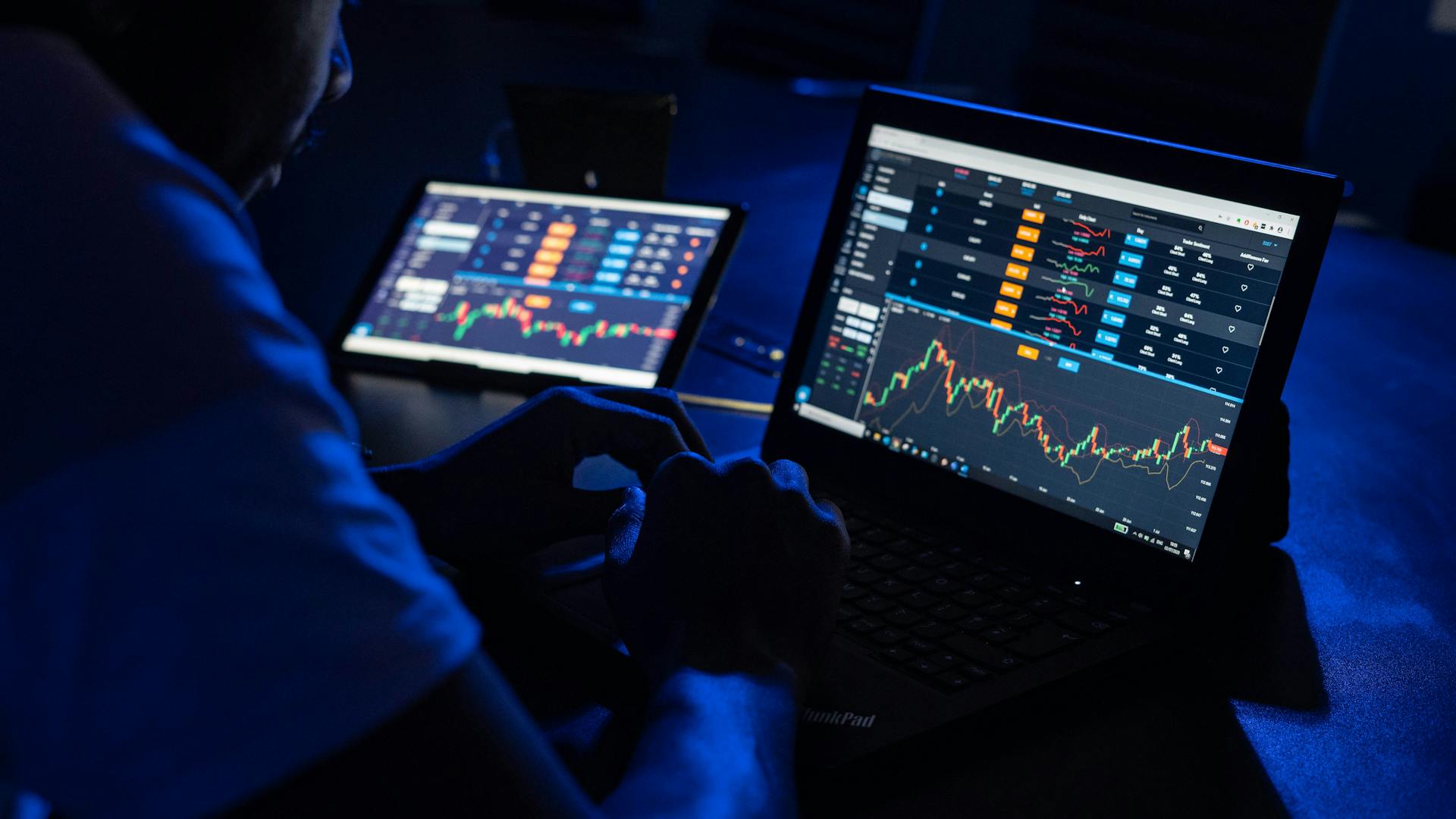
Forex currency trading can be a lucrative venture, but it requires a solid understanding of market trends and strategies. To succeed in this field, traders need to stay informed about global economic events and their impact on currency values.
The foreign exchange market, or forex, is a decentralized market where individuals, businesses, and institutions trade currencies. It's the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $6 trillion.
Market volatility is a key factor to consider when trading currencies. A significant event, such as a central bank's interest rate decision, can cause a currency's value to fluctuate rapidly.
What Is Forex?
Forex is a global marketplace where individuals, businesses, and institutions trade currencies. It's a massive market with a daily turnover of over $6 trillion.
The forex market operates 24/5, meaning it's open for trading from Sunday evening to Friday evening. This allows traders to react to market news and events as they happen.
Forex traders buy and sell currencies in pairs, such as the US dollar against the euro (EUR/USD). The value of one currency is determined by its supply and demand in the global market.
Forex trading involves speculation on the future value of currencies, with traders hoping to profit from changes in exchange rates. This can be done through various trading strategies, including day trading, swing trading, and position trading.
The forex market is decentralized, meaning there is no single exchange or location where trades are executed. Instead, trades are conducted over-the-counter (OTC) through a network of banks, brokers, and other market participants.
For another approach, see: Fiat Currency Exchange Trading
Getting Started
To get started with forex currency trading, you need to understand the basics. A forex pair is made up of two currencies, with one currency being the base and the other being the quote.
You'll also need to know what a pip is - it's the smallest unit of price movement in the forex market. For example, if you're trading the EUR/USD pair and the price moves from 1.1000 to 1.1001, that's a 1 pip movement.
Readers also liked: What Is Pip in Currency Trading
A lot in forex trading refers to the amount of currency being traded. This can vary from 1,000 units to 100,000 units, depending on your account size and trading strategy.
Here are the different types of forex trading:
Essentials for Beginners
To get started with forex trading, you need to understand the basics. A forex pair is a combination of two currencies, with one currency being the base currency and the other being the quote currency.
Forex trading involves buying or selling one currency against another, and the exchange rate between the two currencies determines the price of the trade. The exchange rate is typically quoted as a price in the quote currency, relative to one unit of the base currency.
One pip (price interest point) is the smallest unit of measurement in forex trading, and it's used to calculate the value of a trade. For example, if you're trading the EUR/USD pair and the price moves from 1.1000 to 1.1005, that's a 5-pip move.
Intriguing read: Webull Forex
A lot in forex trading is a standard unit of measurement, equivalent to 100,000 units of the base currency. This is the standard amount that's traded in the market, and it's used as the base for calculating the value of a trade.
Here are the key terms to get you started:
- Base currency: The first currency in a forex pair
- Quote currency: The second currency in a forex pair
- Pip: The smallest unit of measurement in forex trading
- Lot: A standard unit of measurement, equivalent to 100,000 units of the base currency
What Is a Broker?
A forex broker is a platform that gives you access to trade currencies. They charge a fee, usually in the form of a spread, which is the difference between the buy and sell prices.
Forex brokers traditionally acted as middlemen, buying and selling currencies on behalf of their clients. But now, with online trading, you can buy and sell currencies yourself using financial derivatives.
The costs of a trade are factored into the buy and sell prices, so you'll always pay a bit more when buying and a bit less when selling. This spread is a key part of what forex brokers charge.
Related reading: Best Forex Platform
How It Works
In forex trading, you're essentially buying one currency using another. The market price tells you how much of one currency is needed to purchase another. For example, the current market price of the GBP/USD currency pair shows how many US dollars it would take to buy one pound.
Each currency has its own code, which makes it easy to identify as part of a pair. Here are some codes for popular currencies: GBP (British Pound)USD (US Dollar)EUR (Euro)JPY (Japanese Yen)
To buy or sell a currency pair, you need to understand the base and quote currencies. To buy, you expect the price to rise, and to sell, you expect the price to fall.
Consider reading: Gbp Usd Currency News
How It Works
Forex trading works by buying one currency using another, with the market price determining how many of the quote currency it'll cost to buy one of the base currency. The base currency is always on the left of a currency pair, and the quote is always on the right.
Each currency has its own code, which lets traders quickly identify it as part of a pair. Some popular currencies include the euro, the US dollar, the Japanese yen, and the British pound.
To buy a currency pair means you expect the price to rise, indicating that the base currency is strengthening relative to the quote currency. This can be thought of as needing more of the quote currency to buy one of the base currency.
The spread in forex trading is the difference between the buy and sell prices. For example, the buy price might be 1.3428 and the sell price might be 1.3424.
Margin refers to the initial deposit you need to commit in order to open and maintain a leveraged position. A trade on EUR/GBP might only require a 3.33% margin in order for it to be opened.
Here's a list of some popular currency pairs, along with their base and quote currencies:
To sell a currency pair means you expect the price to fall, which would happen if the base currency weakened against the quote currency. This can be thought of as needing fewer of the quote currency to buy one of the base currency.
What Is a Pip?
A pip in forex is usually a one-digit movement in the fourth decimal place of a currency pair.
The movement of a pip can be seen in currency pairs like GBP/USD, which moved from $1.35361 to $1.35371, a single pip.
For JPY crosses, a pip is a change at the second decimal place.
This can be confusing for traders who are used to currency pairs with four decimal places.
Here's an interesting read: Currency Trading Pairs
Market Analysis
The forex market is made up of currencies from all over the world, which can make exchange rate predictions difficult as there are many forces that can contribute to price movements.
A lot of people think that the forex market is driven by the actions of governments, but it's actually a complex interplay of various factors.
The following factors can all have an effect on the forex market: economic indicators, such as interest rates and inflation rates, can influence currency values.
These indicators can have a significant impact on a currency's value, especially if they're not in line with market expectations.
Explore further: Currency Rates Real Time
Central banks play a crucial role in setting interest rates, which can either attract or deter foreign investors.
The strength of a country's economy is also a key factor in determining its currency's value, with strong economies often resulting in higher currency values.
Additionally, global events, such as wars, natural disasters, and political upheavals, can also impact the forex market and currency values.
These events can lead to a loss of confidence in a currency, causing its value to drop.
In conclusion, the forex market is influenced by a multitude of factors, making it a challenging but exciting field to navigate.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is today good for forex trading?
Best days for Forex trading are typically Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday, when market volatility is higher. Check the day of the week to determine if it's a prime trading day
How is the forex market today?
The dollar index is up by 0.14% today, recovering from overnight losses and reaching a 1-week high. This gain is attributed to increased liquidity demand following a slump in equity prices.
Featured Images: pexels.com


