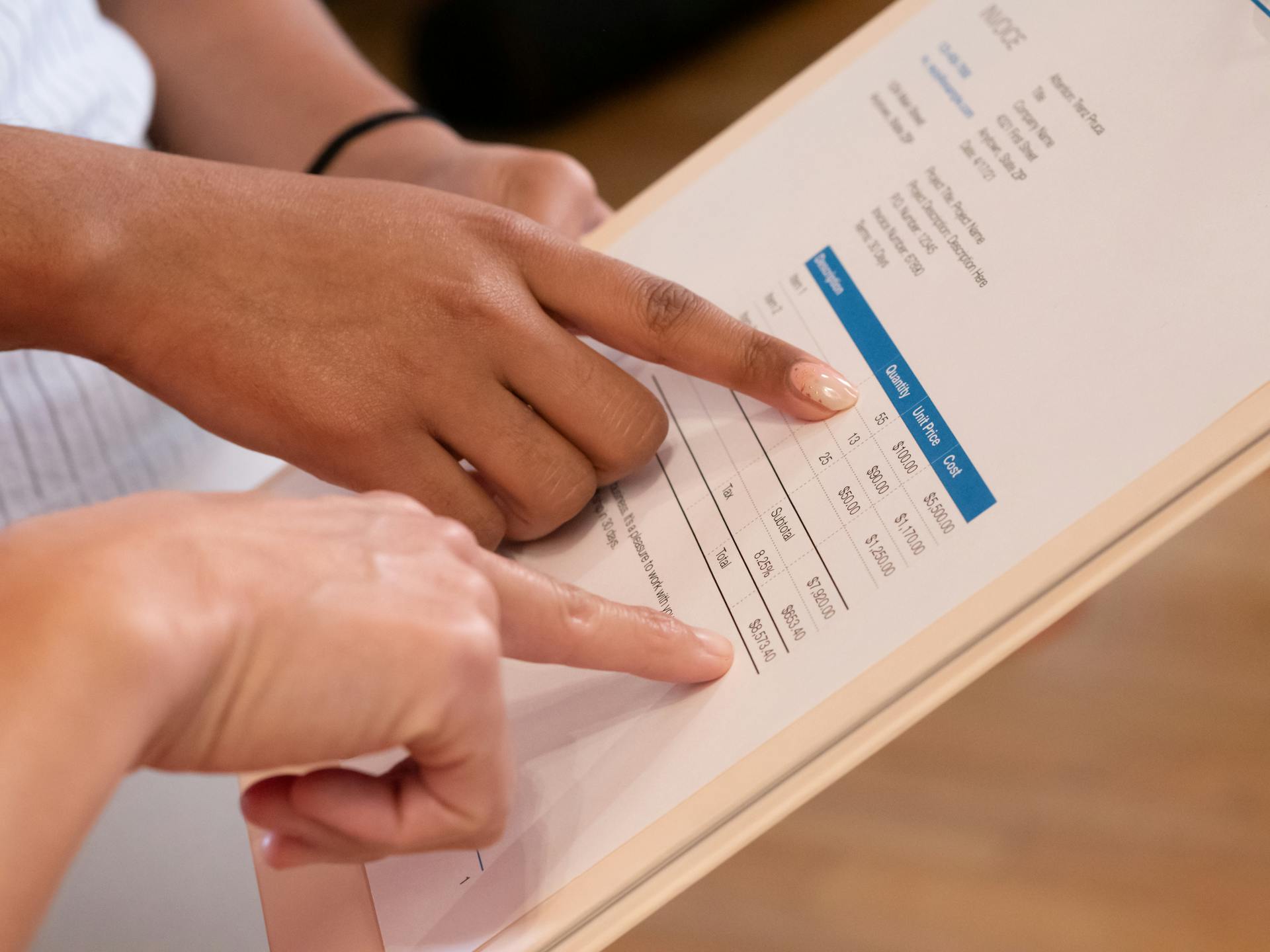
Days of receivables is a crucial metric for businesses to track, and it's not just about getting paid on time. A high days of receivables can indicate that a business is struggling to collect payments from customers.
In fact, a days of receivables of 60 days or more can be a red flag, indicating that a business may be experiencing cash flow problems. This can have a ripple effect on the entire business, making it difficult to pay suppliers, employees, and other bills on time.
Businesses with high days of receivables may also struggle to make timely payments to their own suppliers, which can damage relationships and even lead to late payment fees. This can be a vicious cycle that's hard to break.
For more insights, see: 14 Days Ago
What Are Receivables?
Receivables are amounts owed to a business by customers for goods or services already sold or provided, typically in the form of invoices or accounts receivable.
These amounts are considered assets on a company's balance sheet, as they represent future cash flows that the business can expect to receive.
What Is A/R?

Receivables are essentially the amount of money your customers owe you, and they can be a vital source of cash for your business.
A/R Days, or Accounts Receivable Days, measures the approximate number of days it takes to retrieve cash from customers who paid using credit.
Having a clear understanding of your A/R Days can help you manage your cash flow more effectively.
The A/R Days formula is calculated by dividing the average accounts receivable balance by the net credit sales per day.
Recommended read: Accounts Receivable Financing Factoring
What Is Receivable?
Receivables are a crucial part of a business's financial health, and understanding what they are is essential.
Accounts receivable days is a formula that helps you work out how long it takes to clear your accounts receivable, or the number of days that an invoice will remain outstanding before it’s collected.
This ratio is an excellent way to determine how effective your business is at collecting short-term payments, making it a great tool to add to your financial analysis arsenal.
Take a look at this: Days Sales in Average Receivables Formula
Calculating Receivables

Calculating accounts receivable days is a relatively basic formula: (Accounts Receivable / Revenue) x 365.
This formula helps you understand how long it takes to collect a typical invoice. For example, if Company A has a total of $120,000 in accounts receivable and an annual revenue of $800,000, their accounts receivable days would be 54.75.
To calculate days in accounts receivable, you need to divide the total accounts receivable balance by the average daily charges for a specific period. This can be done by dividing the total charges for that period by the number of days in that period.
Here's a simple formula to calculate days in A/R: Days in A/R = (Total Accounts Receivable / Average Daily Charges). For instance, if you want to calculate the days in A/R for a month, you would divide the total charges for that month by 30.
A lower number of days in A/R indicates that the organization is collecting payments more quickly, which is a positive sign for the financial health of the organization.
Discover more: Accounting Clerk Accounts Receivable

Here's a summary of the two formulas:
Factors Affecting Receivables
The number of days in the average A/R period can significantly affect your accounts receivable days ratio. This can be as simple as changing the time period with which you calculate average A/R from quarterly to annual sales.
Industries such as manufacturing and construction tend to have longer than average accounts receivable days, while retail industries have shorter ones. This is often due to complex billing and payment processes, longer production and delivery times, and customers who are governmental agencies or organizations in the public sector.
Your credit terms can also impact your accounts receivable days ratio. Being more generous with credit terms for low-risk customers may lead to a higher accounts receivable days ratio, but it's essential to weigh this against the risks of issues with cash flow.
Here are some key factors to consider when it comes to credit terms:
A streamlined collections process and effective customer interactions are also crucial in managing accounts receivable days. This includes getting a comprehensive system to capture and record customer interactions, such as calls, emails, and notes.
Customer Base

Your customer base has a significant impact on Accounts Receivable Days. Different industries and customer types exhibit varying payment behaviors, which can affect the overall AR Days.
Large corporations often have more structured payment processes, leading to longer but more predictable payment cycles. This can result in longer AR Days compared to small businesses, which may pay more quickly but with less consistency.
A shift in customer mix can affect a company's overall AR Days. For instance, acquiring more small business clients relative to large corporate customers can lead to changes in payment patterns.
Expanding into new markets can introduce different payment norms and expectations. This can result in longer payment cycles due to factors like currency exchange processes or differing business cultures.
You might enjoy: Record Receipt of Payment for Sales on Account
Economic Conditions
Economic downturns can lead to slower payments from customers, resulting in extended Accounts Receivable Days. Businesses often struggle to collect payments during these times, as clients prioritize critical expenses over prompt payment of invoices.
Worth a look: How to Receive Card Payments

Economic conditions have a significant impact on Accounts Receivable Days. Inflation can erode customers' purchasing power, making it harder for them to pay promptly.
Currency fluctuations can introduce complexity in international trade, prompting customers to delay payments in hopes of more favorable exchange rates. This can make it difficult for businesses to collect payments on time.
In contrast, favorable exchange rates might encourage earlier payments, but this can be unpredictable and unreliable.
Readers also liked: Why Do Mortgage Rates Vary from Day to Day
Seasonal Fluctuations
Seasonal fluctuations can significantly impact a company's Accounts Receivable Days, especially in industries with cyclical sales patterns. Many businesses see a surge in sales during the holiday season, leading to a temporary increase in their accounts receivable balance and AR Days.
For example, a business might experience faster collections in January as customers pay off their holiday purchases. This is a common phenomenon, but it's essential to understand these patterns to make accurate financial forecasts.
Businesses that cater to other companies often experience fluctuations tied to their clients' fiscal year-ends. As organizations manage their financial statements, they may accelerate or delay payments, causing ripple effects in their suppliers' AR Days.
Some businesses might delay payments at the end of their fiscal year to improve their cash position, while others might pay early to utilize remaining budgets. This can lead to unexpected fluctuations in accounts receivable and working capital.
Check this out: Average Days to Collect Receivables Formula
Factors Affecting Amounts

Factors affecting the amount of receivables can be significant, and it's essential to understand what influences them.
The time period used to calculate average A/R can affect the amount of receivables, with longer periods resulting in higher amounts.
Industries such as manufacturing and construction tend to have longer accounts receivable days, while retail has shorter ones, often due to complex billing and payment processes.
Your credit terms can also impact the amount of receivables, with more generous terms leading to higher amounts.
Late payment penalties can motivate customers to pay on time, and incentivizing early payments can also help reduce the amount of receivables.
Here are some common credit policy changes that can affect the amount of receivables:
Best Practices for Improving Receivables
Accurate and timely billing is crucial to reducing days in accounts receivable. This means submitting claims as soon as possible after services are rendered and including all necessary information.
Clear and concise claims are essential to avoid rejections or denials. Claims should be free of errors and include all necessary information.

Effective denial management is vital to reducing days in accounts receivable. This includes identifying the root cause of denials, appealing denied claims, and tracking and analyzing denial trends.
Follow-up is critical to collecting payment. Staff should be trained to follow up on unpaid claims in a timely manner and be persistent in their efforts to collect payment.
Accurate and timely posting of payments is essential. Payments should be posted as soon as they are received, and all necessary information should be included in the payment posting.
Effective patient communication can help reduce days in accounts receivable. This includes providing clear and concise statements, offering payment plans, and providing financial counseling when necessary.
Ongoing monitoring and analysis of accounts receivable days is essential to identifying areas for improvement. This includes tracking accounts receivable days over time, analyzing trends, and identifying areas for improvement.
Offering ACH debit can significantly reduce the time it takes to collect outstanding invoices. This enables you to take payment directly from your customer's account whenever payment is due.
Revenue cycle software can automate and streamline the billing and collections process. This can help reduce days in accounts receivable by identifying and resolving billing errors and streamlining the collections process.
For another approach, see: Accounts Receivable Financing
Understanding Receivable Ratios

The accounts receivable days ratio is a key metric that indicates how efficiently a business collects its outstanding invoices. It's typically between 30 and 70 days, with 30 considered low.
A ratio of 30 days or less is considered ideal, as it shows that a business is collecting its debts quickly. This is especially important in the healthcare industry, where a longer payment cycle can lead to cash flow problems.
In the healthcare industry, the benchmark for days in accounts receivable is 30 days or less. This is because a longer payment cycle can indicate issues with billing and collections processes.
A higher ratio can lead to decreased revenue and cash flow problems, making it essential to keep this metric low.
You might like: Receivables Turnover Ratio
Importance and Benefits
Managing days of receivables is crucial for any business. By doing so, companies can gain clear visibility of their overall financial position.
Better management of accounts receivable days through automation helps eliminate mistakes that delay payments. Manually invoicing customers can lead to errors, which further delay payments.

Communicating consistently with customers before the due date can help prevent delinquencies. Clearly communicate the amount owed, the date it's due, and the type of payment accepted.
Automating accounts receivable processes can reduce days sales outstanding (DSO). This is especially true when dealing with customers who have unique billing requirements.
Reducing days sales outstanding (DSO) leads to more timely payments. This, in turn, results in more cash on hand and easier cash flow management.
Here are some benefits of managing accounts receivable days:
- Gain accounts receivable efficiencies and predictable revenue streams
- Lower accounts receivable expenses
- Improve cash flow management
Tools and Assistance
Gaviiti's A/R management and automation platform helps streamline the collections process by eliminating manual tasks and automating the entire A/R process, from invoice distribution to collections analytics.
Automated invoicing and payment systems can significantly impact a company's Accounts Receivable Days by reducing errors and delays that often contribute to extended AR Days.
With Gaviiti's platform, you can take a proactive approach by defining and automating collections actions based on predefined criteria, such as due date, aging of invoices, payment history, or credit terms.
Explore further: Best Day Trader Platform

Gaviiti's platform also includes intelligent prioritization, which minimizes bad debt and maximizes recovery by leveraging algorithms to prioritize collections activities based on factors such as payment history, customer creditworthiness, and the amount outstanding.
Here are some key features of Gaviiti's A/R management and automation platform:
- Single source of truth for A/R performance
- Automated collections actions
- Intelligent prioritization
By leveraging these technological solutions, companies can reduce their AR Days and improve overall efficiency in their accounts receivable management and customer experience, leading to better cash flow and stronger customer relationships.
Technology and Process
Technology and process changes can significantly impact a company's Accounts Receivable Days. Implementing automated invoicing and payment systems can streamline the entire billing process, reducing errors and delays.
Electronic payment options integrated into these systems make it easier for customers to pay quickly and conveniently. Improved communication tools play a crucial role in enhancing follow-up processes.
Automating the process can reduce the time it takes to onboard a new customer from four days or longer to just a few seconds. This can save both time and money.

TreviPay's payments technology can handle underwriting, credit lines, onboarding, and collections, freeing up working capital and reducing risk. It can also extend terms on your behalf.
With TreviPay, companies can receive payment in as little as 48 hours, while its customer support team handles invoicing, dunning, collections, and customer disputes. This can significantly improve cash flow management.
Gaviti Calculation Assistance
Gaviti's A/R management and automation platform helps you take control of your accounts receivable days by eliminating manual processes and automating the entire A/R process.
You can use Gaviti's automated A/R management and automation module to define and automate collections actions based on predefined criteria, such as due date, aging of invoices, payment history, or credit terms.
Gaviti's intelligent prioritization feature minimizes bad debt and maximizes recovery by leveraging intelligent algorithms to prioritize collections activities based on factors such as payment history, customer creditworthiness, and the amount outstanding.
To calculate accounts receivable days, you can use the formula: Accounts Receivable Days = (Accounts Receivable / Revenue) x 365.
For example, if Company A has a total of $120,000 in their accounts receivable, along with an annual revenue of $800,000, the calculation would be: Accounts Receivable Days = (120,000 / 800,000) x 365 = 54.75.
Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R) is calculated by dividing the total accounts receivable balance by the average daily charges for a specific period.
The formula for calculating Days in A/R is:Days in A/R = (Total Accounts Receivable / Average Daily Charges)
Here's a quick reference guide to help you calculate accounts receivable days:
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you calculate days in receivables?
To calculate days in receivables, we divide the sum of current and prior period accounts receivable balances by current period revenue, then multiply by 365 days. This calculation provides a snapshot of how long it takes to collect outstanding invoices.
What is the difference between DSO and AR days?
DSO (Days Sales Outstanding) measures collection speed, while DSO days (also known as AR days) focuses on the average time to collect receivables, with the latter being a more specific metric.
What is a good AR/days ratio?
A good accounts receivable days ratio typically falls between 30 and 70 days, with lower ratios indicating more efficient collections. If your ratio exceeds 70 days, it may indicate a need to improve your invoicing and payment processes.
What is the formula for accounts receivable?
Accounts receivable is calculated using two key metrics: net annual credit sales and average accounts receivable. The formula is: Accounts Receivable = (Net Annual Credit Sales) / (Average Accounts Receivable).
What is the formula for DSO 12 months?
DSO (Days Sales Outstanding) is calculated as (Average Accounts Receivable / Revenue) x 365 days. This formula is used to determine the average number of days it takes to collect accounts receivable over a 12-month period.
Sources
- https://www.wallstreetprep.com/knowledge/ar-days/
- https://www.trevipay.com/resource-center/blog/better-managing-accounts-receivable-days-strengthens-your-financial-position-improves-cash-flow/
- https://gaviti.com/glossary/accounts-receivable-days/
- https://gocardless.com/en-us/guides/posts/what-is-the-accounts-receivable-days-formula/
- https://www.mdclarity.com/rcm-metrics/days-in-accounts-receivable-ar
Featured Images: pexels.com