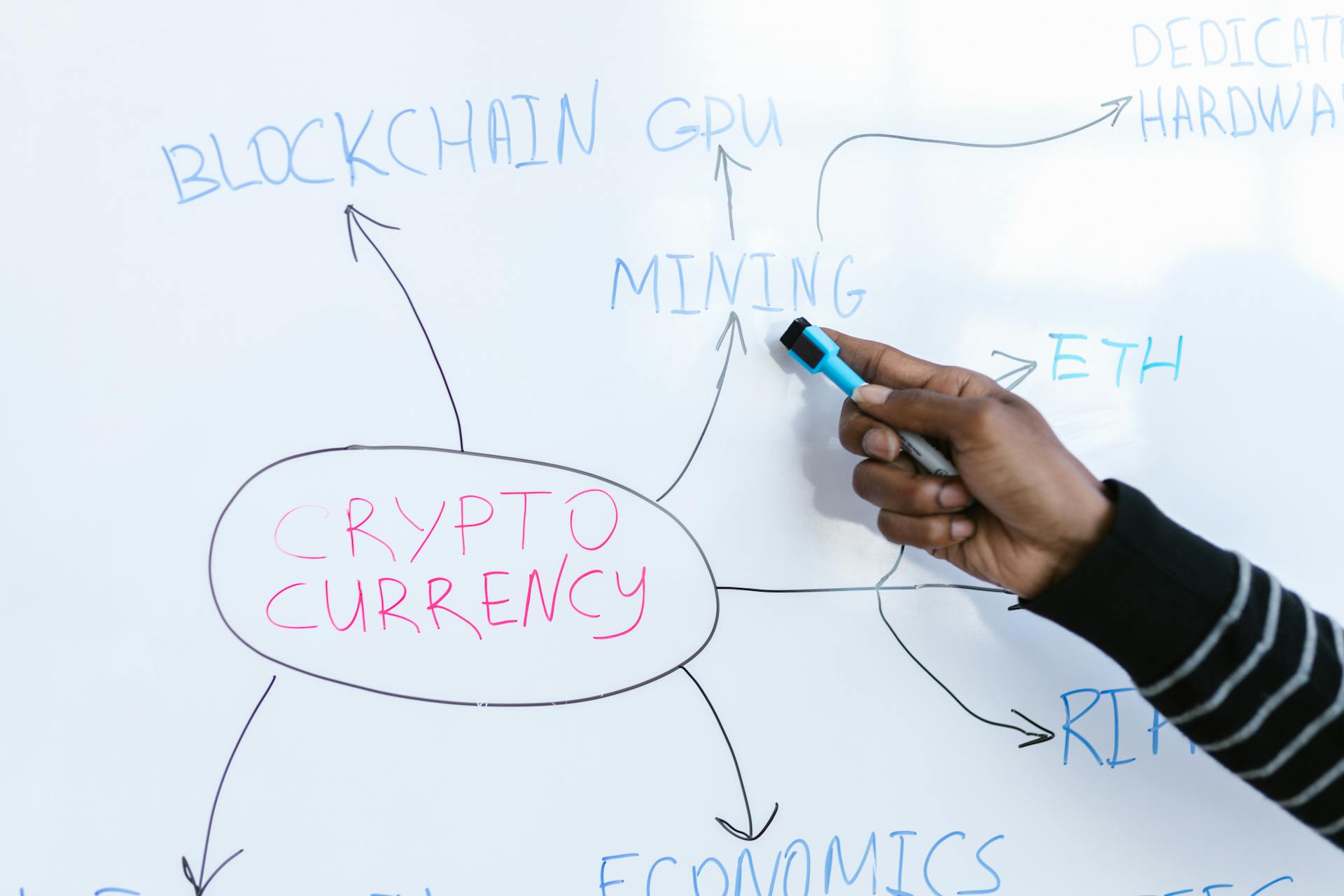
Cryptocoin is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security and is decentralized, meaning it's not controlled by any government or financial institution.
It's like the cash in your wallet, but instead of physical bills and coins, it exists only on computers and phones.
Cryptocoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger called a blockchain, which helps ensure the integrity and security of the transactions.
This decentralized system allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks.
What is Cryptocoin?
Cryptocoin is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography to secure transactions. It's a decentralized system, meaning there's no central authority in charge.
To be more specific, a cryptocoin system meets six conditions. Here are the key ones:
- The system doesn't require a central authority, its state is maintained through distributed consensus.
- The system keeps track of cryptocoin units and who owns them.
- The system decides whether new cryptocoin units can be created and how they're distributed.
- Ownership of cryptocoin units can be proven using cryptography alone.
- The system allows transactions to change ownership of cryptocoin units, and only the current owner can initiate these transactions.
- If there are conflicting instructions to change the same cryptocoin units, the system will only process one of them.
Cryptocoin doesn't have a central issuer or regulator. Instead, it uses a decentralized system to record transactions and issue new units.
Types of Cryptocoin
Cryptocoin types are an essential part of understanding the cryptocurrency world. Knowing the type of cryptocoin can help you decide if it's worth investing in, as a cryptocoin with a purpose is likely to be less risky.
Many cryptocoins were created to facilitate work done on the blockchain they are built on. For example, Ethereum's ether was designed to be used as payment for validating transactions and opening blocks. Utility tokens like XRP and ETH serve specific functions on their respective blockchains.
Here are some common types of cryptocoins:
- Utility: These tokens serve specific functions on their respective blockchains.
- Transactional: These tokens are designed to be used as a payment method, like Bitcoin.
- Governance: These tokens represent voting or other rights on a blockchain, such as Uniswap.
- Platform: These tokens support applications built to use a blockchain, like Solana.
- Security tokens: These tokens represent ownership of an asset, like a stock that has been tokenized.
Altcoins
Altcoins are alternative cryptocurrencies that emerged after the early innovation of bitcoin. Over 5,000 cryptocurrencies exist, with altcoins making up the vast majority of them.
Altcoins often have underlying differences compared to bitcoin, such as Litecoin's faster block processing time of 2.5 minutes, which allows for quicker transaction confirmation. Ethereum, another popular altcoin, boasts smart contract functionality that enables decentralized applications to run on its blockchain.
Ethereum was the most used blockchain in 2020, according to Bloomberg News, and it had the largest following of any altcoin in 2016, according to the New York Times. This popularity has led to significant market price rallies across multiple altcoin markets, often referred to as an "altseason".
Some notable altcoins include Ethereum, Litecoin, and XRP, which serve specific functions on their respective blockchains. XRP, for example, facilitates transfers between different geographies for financial institutions.
For more insights, see: Dash Altcoin News
Memecoins
Memecoins are a category of cryptocurrencies that originated from Internet memes or jokes.
The most notable example is Dogecoin, which features the Shiba Inu dog from the Doge meme.
Memecoins are known for extreme volatility, with prices fluctuating wildly over time.
Dogecoin's record-high value was 73 cents, but it had plunged to 13 cents by mid-2024.
Scams are prolific among memecoins, making it essential to approach these cryptocurrencies with caution.
Discover more: Cryptocurrencies Events
Blockchain and Technology
Blockchain technology is a secure, distributed ledger that records transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way. It's like a digital record book that can't be altered without the majority of the network agreeing to the change.
Each block in the blockchain contains a hash pointer linking it to the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. This design makes it inherently resistant to modification of the data.
Blockchain technology is also secure by design, with high Byzantine fault tolerance, which means it's resistant to malicious attacks and can still function even if some nodes in the network fail. Decentralized consensus has been achieved with blockchain technology.
However, there are also purely technical limitations to consider. High up-front costs to miners in the form of specialized hardware and software can be a barrier to entry. Cryptocurrency transactions are normally irreversible after a number of blocks confirm the transaction, so be sure to double-check your transactions before confirming them.
Physical Crypto
Physical crypto has been made as promotional items and some have become collectibles. Some of these have a private key embedded in them to access crypto worth a few dollars.
Physical representations of cryptocurrency do not hold any value by themselves. They are only utilized for collectable purposes.
Investment funds that hold crypto purchased from crypto exchanges put their crypto holdings in a specialized bank called a "custodian". This is referred to as "physical bitcoin" in the finance industry.
Blockchain
A blockchain is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked and secured using cryptography. Each block contains a hash pointer as a link to a previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. By design, blockchains are inherently resistant to modification of the data.
Blockchains are secure by design and are an example of a distributed computing system with high Byzantine fault tolerance. Decentralized consensus has therefore been achieved with a blockchain.
A blockchain is an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way. This is made possible by a peer-to-peer network collectively adhering to a protocol for validating new blocks.
Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires collusion of the network majority. This ensures the integrity and security of the blockchain.
The size of a blockchain can grow indefinitely, making it a virtually limitless repository of information. This is due to the fact that new blocks are constantly being added to the end of the chain.
On a similar theme: New Bitcoins
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees for cryptocurrency depend mainly on the supply of network capacity at the time, versus the demand from the currency holder for a faster transaction.
Some cryptocurrency exchanges, like LiteBit, previously allowed users to choose between different presets of transaction fee values during the currency conversion.
The recommended fee suggested by the network often depends on the time of day, due to depending on network load.
For Ethereum, transaction fees differ by computational complexity, bandwidth use, and storage needs.
In February 2023, the median transaction fee for Ether corresponded to $2.2845.
Bitcoin transaction fees, on the other hand, differ by transaction size and whether the transaction uses SegWit.
The median transaction fee for bitcoin in February 2023 corresponded to $0.659.
Some cryptocurrencies, like Nano (XNO), have no transaction fees and instead rely on client-side proof-of-work as the transaction prioritization and anti-spam mechanism.
Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps are a mechanism where one cryptocurrency can be exchanged directly for another cryptocurrency without the need for a trusted third party, such as an exchange.
This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about cryptocurrency trading, making it faster, cheaper, and more secure.
Atomic swaps allow for peer-to-peer exchanges, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of market manipulation.
Databases
Databases are an essential part of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, providing fast access to crypto market data.
They're often used in conjunction with blockchains, but some databases store crypto market data independently.
CoinMarketCap, CoinGecko, BraveNewCoin, and Cryptocompare are four popular cryptocurrency market databases that offer this service.
These databases are known for their speed, as they don't require the verification process that blockchains do.
Cryptocoin Economy
Cryptocurrencies are used primarily outside banking and governmental institutions, which is a significant departure from traditional financial systems. This is likely due to the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies, allowing for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries.
The exchange of cryptocurrencies takes place over the internet, providing a level of convenience and accessibility that traditional financial systems often can't match.
History
The concept of cryptocurrency has been around for decades. David Chaum conceived of a type of cryptographic electronic money called ecash in 1983.
In 1995, Chaum implemented ecash through Digicash, an early form of cryptographic electronic payments. This system required user software to withdraw notes from a bank and designate specific encrypted keys before sending them to a recipient.
Curious to learn more? Check out: Ripple Electronic Currency
The National Security Agency published a paper in 1996, describing a cryptocurrency system. The paper was first published in an MIT mailing list and later in The American Law Review.
Wei Dai described "b-money" in 1998, an anonymous, distributed electronic cash system. Nick Szabo described bit gold, an electronic currency system that required users to complete a proof of work function.
In January 2009, bitcoin was created by a pseudonymous developer, Satoshi Nakamoto. It used SHA-256, a cryptographic hash function, in its proof-of-work scheme.
Cryptocurrency has experienced several periods of growth and retraction, including market crashes in 2011, 2013-2014/15, 2017-2018, and 2021-2023.
The UK Treasury commissioned a study on cryptocurrencies in 2014, to report on their role in the UK economy and whether regulation should be considered.
Stablecoins
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable level of purchasing power.
Not all stablecoins are foolproof, as we've seen with the collapse of Terra's UST, which fell from $1 to 26 cents in May 2022.
This collapse resulted in the loss of nearly $40B invested in the Terra and Luna coins.
The subsequent failure of Terraform Labs led to South Korean prosecutors requesting an Interpol Red Notice against the company's founder, Do Kwon, in September 2022.
Regulatory frameworks for stablecoins are being shaped in countries like Hong Kong, with expectations for a framework to be in place by 2023/24.
Economics
Cryptocurrencies are used primarily outside banking and governmental institutions and are exchanged over the Internet.
One of the key characteristics of cryptocurrencies is their ability to operate independently of traditional financial systems. This allows for a level of freedom and flexibility that's not always available with traditional currencies.
Cryptocurrencies are not issued or backed by any government or institution, which can make them more appealing to those looking for an alternative to traditional financial systems.
Initial Coin Offerings
Initial Coin Offerings are a way for new cryptocurrency ventures to raise funds, but they're often shrouded in controversy. An ICO can be used by startups to avoid regulation.
In many jurisdictions, including the U.S. and Canada, securities regulators have indicated that if a coin or token is an "investment contract", it's considered a security and is subject to regulation. This means that if you're investing in an ICO, you should be aware that it may be subject to certain rules and guidelines.
ICOs often involve selling a percentage of cryptocurrency, usually in the form of "tokens", to early backers in exchange for legal tender or other cryptocurrencies. This can be a way for startups to raise funds quickly and efficiently.
Four of the 10 biggest proposed ICOs have used Switzerland as a base, where they're frequently registered as non-profit foundations. This is likely because Switzerland has taken a "balanced approach" to ICO projects, allowing legitimate innovators to navigate the regulatory landscape.
Social Aspects
Bitcoin's social and political aspects are complex and multifaceted. Libertarians and anarcho-capitalists were attracted to the philosophical idea behind bitcoin.
Early bitcoin supporters saw it as a way to separate money from the state, with Roger Ver saying "at first, almost everyone who got involved did so for philosophical reasons." Economist Paul Krugman argues that cryptocurrencies like bitcoin are "something of a cult" based in "paranoid fantasies" of government power.
The ideas influencing bitcoin advocates emerge from right-wing extremist movements, such as the Liberty Lobby and the John Birch Society, and their anti-Central Bank rhetoric. Ron Paul and Tea Party-style libertarianism also played a role in shaping the ideology behind bitcoin.
Satoshi Nakamoto, bitcoin's founder, supported the idea that cryptocurrencies go well with libertarianism, saying "it's very attractive to the libertarian viewpoint if we can explain it properly."
Cryptocoin Security and Risks
Cryptocoin security is a concern due to the rise of cryptocurrency crime. Unfortunately, cryptocurrency scams are on the rise, including fake websites, virtual Ponzi schemes, and romance scams.
One of the most common scams is the fake website scam, where scammers create a fake site that promises massive returns on investment. In 2019, the BitClub Network scam raised over $700 million before its perpetrators were indicted.
Cryptocoin owners can store their assets safely in crypto wallets, which are physical devices or online software used to store private keys securely. There are two types of wallets: hot wallets, which use online software to protect private keys, and cold wallets, which rely on offline electronic devices.
To protect yourself from hacks or theft, consider using a comprehensive antivirus, such as Kaspersky Internet Security, which defends against malware infections, spyware, and data theft.
Transactions in cryptocoin require a two-factor authentication process, including a username and password, and an authentication code sent via text to your personal cell phone. However, this does not mean cryptocoin is un-hackable, as several high-dollar hacks have cost cryptocurrency start-ups heavily.
Here are some common cryptocoin security risks:
- Fake websites and Ponzi schemes
- Romance scams
- Hacking and data theft
- Volatility in cryptocoin value
It's essential to be aware of these risks and take steps to protect yourself, such as using reputable exchanges, storing assets safely, and being cautious of suspicious activity.
Anonymity
Bitcoin is pseudonymous, rather than anonymous, meaning its owners are not immediately identifiable, but all transactions are publicly available in the blockchain.
Cryptocurrency exchanges are often required by law to collect the personal information of their users.
Some cryptocurrencies implement additional measures to increase privacy, such as using zero-knowledge proofs.
Monero, Zerocoin, Zerocash, and CryptoNote are examples of cryptocurrencies that offer enhanced anonymity features.
A recent study in 2020 demonstrated how anonymity techniques in cryptocurrencies are not sufficient safeguards against privacy attacks.
Researchers suggested new cryptographic schemes and mechanisms for hiding the IP address of the source to improve privacy.
Loss, Theft, and Fraud
Loss of funds is a significant risk when investing in cryptocurrencies. One in 10 potential cryptocurrency buyers are unaware of consumer warnings on the FCA website.
The lack of consumer protection is a major concern. Unlike traditional financial products, there is no intermediary with the power to limit consumer losses if bitcoins are lost or stolen.
Cryptocurrency scams are on the rise, with fake websites and virtual Ponzi schemes being used to deceive investors. The BitClub Network scam operation raised over $700 million before its perpetrators were indicted in December 2019.
Romance scams are also a growing concern, with the FBI warning of a trend in online dating scams where tricksters persuade people to invest or trade in virtual currencies. The FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Centre fielded over 1,800 reports of crypto-focused romance scams in the first seven months of 2021, with losses reaching $133 million.
Several high-dollar hacks have cost cryptocurrency start-ups heavily, with hackers hitting Coincheck to the tune of $534 million and BitGrail for $195 million in 2018.
Money Laundering
Money laundering is a significant concern in the cryptocurrency world. In 2021, criminals laundered a staggering $8.6 billion worth of cryptocurrency, a 30% increase from the previous year.
A small group of purpose-built centralized exchanges is often used for sending and receiving illicit cryptocurrency. These exchanges received 47% of funds sent by crime-linked addresses in 2021.
The majority of cryptocurrency theft in 2021, 72%, involved embezzlement from DeFi protocols, with over $2.2 billion stolen.
Federation Tower in Moscow City is home to numerous cryptocurrency businesses suspected of facilitating extensive money laundering. These businesses include Garantex, Eggchange, Cashbank, and others.
The dark web marketplace Hydra, powered by cryptocurrency, generated over $1 billion in sales in 2020. It demands that sellers liquidate cryptocurrency through specific regional exchanges, making it difficult for investigators to track the money.
A significant portion of ransomware revenue, over $400 million worth of cryptocurrency, went to software strains likely affiliated with Russia in 2021. This represents almost 74% of ransomware revenue that year.
RenBridge, an unregulated alternative to exchanges, was found to be responsible for laundering at least $540 million since 2020. It's especially popular with individuals attempting to launder money from theft.
Consider reading: Rocket Money Mint
Darknet
Darknet markets are a type of online black market that use cryptocurrencies for transactions.
The original Silk Road was shut down in October 2013, but two more versions have been in use since then.
Darknet markets have seen a significant increase in popularity, with the number of prominent dark markets rising from four to twelve in the year following the initial shutdown of Silk Road.
The amount of drug listings on these markets increased from 18,000 to 32,000 during the same time period.
Cryptocurrencies used in dark markets are not clearly or legally classified in almost all parts of the world, putting pressure on law enforcement agencies to adapt to the shifting drug trade.
Wash Trades
Wash trades are a serious problem in the crypto world. Up to 80% of trades on unregulated cryptocurrency exchanges could be wash trades, according to a 2019 study.
This means that some people are essentially trading with themselves to inflate volume and manipulate prices. It's a way to artificially boost the value of a cryptocurrency.
A report by Bitwise Asset Management found that 95% of all bitcoin trading volume reported on major website CoinMarketCap was artificially generated. This is a staggering number that highlights the extent of the issue.
Only 10 out of 81 exchanges studied provided legitimate volume figures, according to the same report. This suggests that many exchanges are not being honest about their trading volumes.
How to Store
Storing your cryptocurrency safely is crucial to protect it from hacks or theft. You can store it in a crypto wallet, which is a physical device or online software used to store the private keys to your cryptocurrencies securely.
Some exchanges provide wallet services, making it easy to store directly through the platform. However, not all exchanges or brokers automatically provide wallet services for you.
There are different types of wallets to choose from, including hot wallets and cold wallets. Hot wallets use online software to protect your private keys, while cold wallets rely on offline electronic devices.
Hot wallets don't charge fees, but cold wallets typically do. Typically, cold wallets tend to charge fees, while hot wallets don't.
You can choose between a hot wallet and a cold wallet based on your needs and preferences. Consider the level of security you need and the fees associated with each type of wallet.
Regulation and Legality
Regulations around cryptocurrencies vary greatly from country to country, with at least 9 countries having an "absolute ban" on trading or using cryptocurrencies.
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has defined cryptocurrency-related services as "virtual asset service providers" (VASPs) and recommended that they be regulated with the same money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) requirements as financial institutions.
In the European Union, the European Commission published a digital finance strategy in September 2020, which included a draft regulation on Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) to provide a comprehensive regulatory framework for digital assets.
The IMF is seeking a coordinated, consistent, and comprehensive approach to supervising cryptocurrencies to maintain financial stability while enjoying the benefits of the underlying technological innovations.
In the United States, the US Congress advanced a bill in May 2024 to provide regulatory clarity for digital assets, defining responsibilities between various US agencies.
Consider reading: Digital Bolivar
U.S. Tax Status
In the United States, the tax status of cryptocurrencies is clear: they are considered property for tax purposes.
The IRS ruled on March 25, 2014, that bitcoin, in particular, will be treated as property, subject to capital gains tax.
This means that if you buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies, you'll need to report the gains or losses on your tax return.
For example, if you buy 10 bitcoins in 2022 and sell them in 2023 for a higher price, you'll need to report the profit as capital gains.
The IRS considers cryptocurrencies commodities, just like stocks or real estate, so you'll need to keep track of your transactions and report them accordingly.
Here's a quick rundown of the key points to keep in mind:
Increasing Regulation
Increasing regulation is becoming a reality in the world of cryptocurrencies. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has defined cryptocurrency-related services as "virtual asset service providers" (VASPs) and recommended that they be regulated with the same money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) requirements as financial institutions.
The FATF and financial regulators were informed as the IVMS 101 data model was developed to facilitate communication between VASPs. In June 2020, the FATF updated its guidance to include the "Travel Rule" for cryptocurrencies, mandating that VASPs obtain, hold, and exchange information about the originators and beneficiaries of virtual asset transfers.
In December 2020, the IVMS 101 data model had yet to be finalized and ratified by the three global standard setting bodies that created it. The European Commission published a digital finance strategy in September 2020, which included a draft regulation on Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA).
The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision proposed that banks holding cryptocurrency assets must set aside capital to cover all potential losses in June 2021. This is a more extreme standard than banks are usually held to when it comes to other assets, but it's still just a proposal.
The IMF is seeking a coordinated, consistent, and comprehensive approach to supervising cryptocurrencies, aiming to maintain financial stability while enjoying the benefits of technological innovations.
You might enjoy: Standard Chartered Bitcoin
Legality
The legality of cryptocurrencies varies greatly from country to country, and in many places, it's still undefined or changing. At least one study has shown that broad generalizations about the use of bitcoin in illicit finance are significantly overstated.
In 2021, the Library of Congress reported that an "absolute ban" on trading or using cryptocurrencies applies in 9 countries, including Algeria, Bangladesh, and China. An "implicit ban" applies in another 39 countries or regions.
The classification of bitcoin has been inconsistent, with different government agencies, departments, and courts classifying it differently. In China, the Central Bank banned the handling of bitcoins by financial institutions in 2014.
In the United States and Canada, state and provincial securities regulators are investigating "Bitcoin scams" and ICOs in 40 jurisdictions. The US Congress is expected to prioritize cryptocurrency legislation in 2025, with a focus on the Stablecoin Act and the Financial Innovation and Technology for the 21st Century (FIT21) Act.
Regulations and bans that apply to bitcoin probably extend to similar cryptocurrency systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which crypto coins to buy now?
For those looking to invest in the latest cryptocurrencies, consider buying Sei (SEI), Ripple (XRP), and Aave (AAVE) for potential growth and stability. Research each coin's unique features and market trends before making an informed investment decision.
Will crypto rise again in 2025?
There is potential for cryptocurrency prices to rise in 2025, driven by increasing market confidence and demand. Analysts like Egrag predict significant gains, with some forecasting XRP to reach $50.
How much is 1 coin crypto worth?
As of now, 1COIN is worth approximately $0.000000000008566. However, cryptocurrency prices can fluctuate rapidly, so it's essential to stay up-to-date for the most current value.
Sources
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryptocurrency
- https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/definitions/what-is-cryptocurrency
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/cryptocurrency.asp
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/cryptocurrency/top-10-cryptocurrencies/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_cryptocurrencies
Featured Images: pexels.com